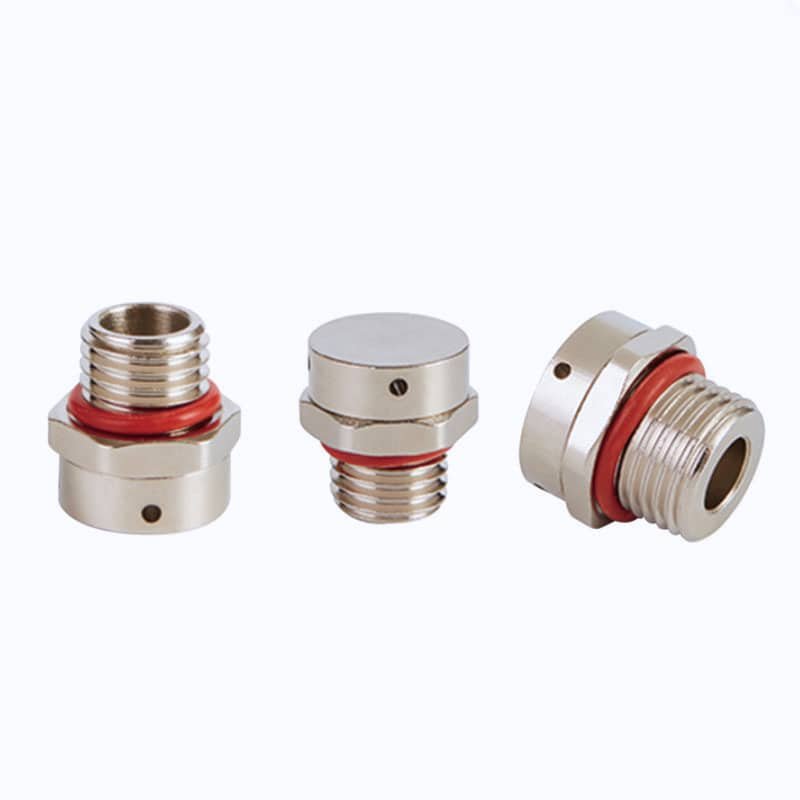
Moisture buildup and pressure changes destroy thousands of outdoor enclosures every year, costing businesses millions in equipment replacement and downtime. Most facility managers don’t realize that a simple $5 component could prevent 90% of these failures.
Oddychający korek wentylacyjny wydłuża żywotność obudowy zewnętrznej, zapobiegając kondensacji wilgoci i wzrostowi ciśnienia, które powodują awarie uszczelek, korozję i uszkodzenia elementów elektronicznych. Ten niewielki, ale krytyczny element umożliwia wymianę powietrza, jednocześnie blokując wnikanie wody, utrzymując optymalne warunki wewnętrzne w trudnych warunkach zewnętrznych.
Last week, I received a frustrated call from Marcus, a maintenance manager at a solar farm in Arizona. His control panel enclosures were failing after just 18 months due to internal condensation and corrosion. The expensive IP65-rated1 enclosures couldn’t handle the extreme temperature swings without proper pressure equalization. A simple breathable vent plug solution could have saved him $15,000 in replacement costs. 😤
Spis treści
- Why Do Outdoor Enclosures Fail Without Proper Venting?
- How Do Breathable Vent Plugs Work to Protect Enclosures?
- What Types of Vent Plugs Are Best for Different Applications?
- How Do You Choose and Install the Right Vent Plug?
- What Maintenance Do Vent Plugs Require for Long-Term Performance?
- FAQs About Outdoor Enclosure Vent Plugs
Why Do Outdoor Enclosures Fail Without Proper Venting?
Understanding the root causes of enclosure failure is essential for implementing effective protection strategies that extend equipment life and reduce maintenance costs.
Outdoor enclosures fail without proper venting due to pressure differentials caused by temperature changes, which create condensation, compromise seals, and allow moisture ingress that corrodes internal components. Temperature cycling between day and night can create pressure changes of 10-15%, stressing gaskets and drawing humid air into sealed enclosures.
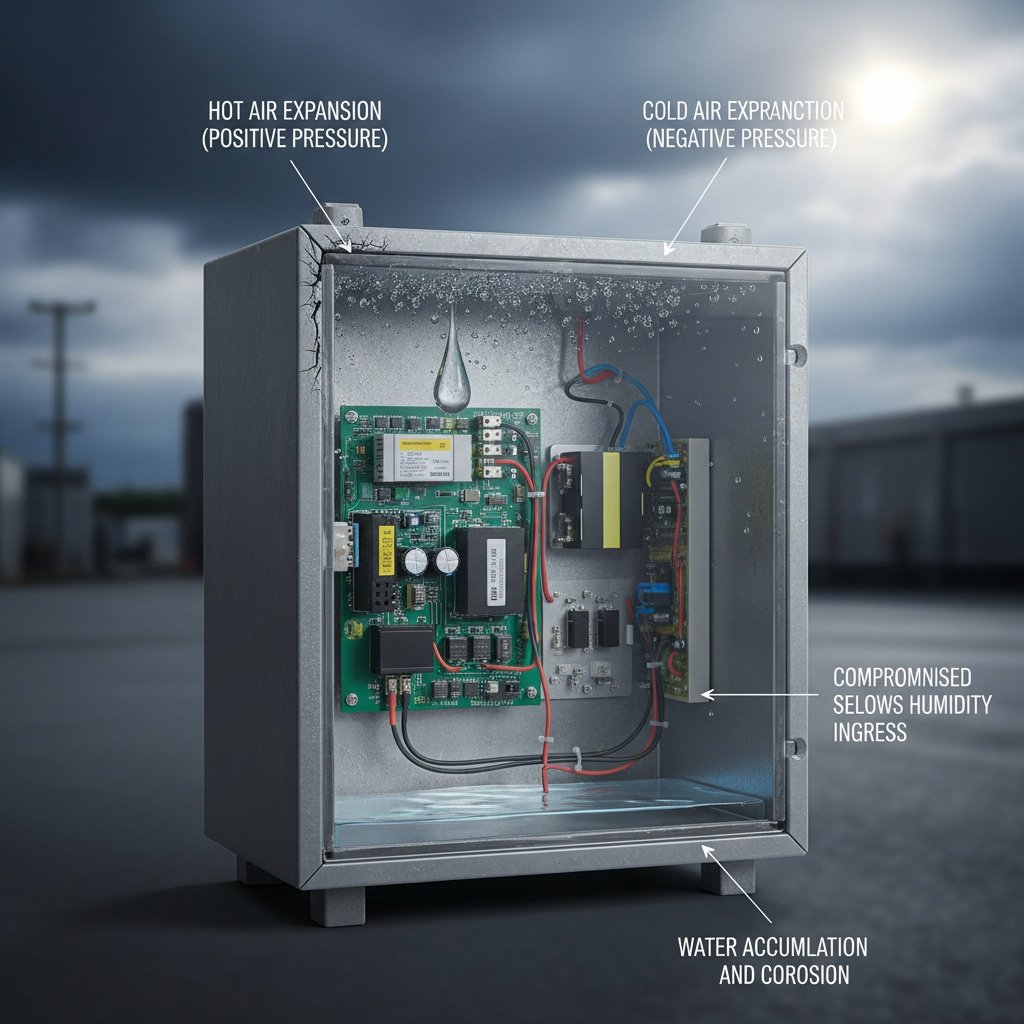
Temperature-Induced Pressure Changes
Daily Temperature Cycling: Outdoor enclosures experience significant temperature variations, often ranging from 10°C at night to 50°C during peak sun exposure. As internal air heats up, it expands and creates positive pressure. When temperatures drop rapidly, the air contracts, creating negative pressure that can draw moisture through compromised seals.
Zmiany sezonowe: Annual temperature ranges can span from -20°C to 60°C in extreme climates, creating even more severe pressure cycling. Each cycle stresses enclosure seals and gaskets, gradually reducing their effectiveness over time.
Rapid Weather Changes: Storm fronts and cloud cover can cause temperature drops of 20°C in minutes, creating sudden pressure differentials that can damage seals or draw moisture into the enclosure through microscopic gaps.
Moisture and Condensation Problems
Internal Condensation Formation: When warm, humid air inside an enclosure cools rapidly, it reaches its punkt rosy2 and forms condensation on internal surfaces. This moisture directly contacts electrical components, causing corrosion, short circuits, and component failure.
Humidity Infiltration: Even small amounts of humid air drawn into an enclosure during pressure changes can create significant moisture problems. A sealed enclosure with just 1% air exchange per temperature cycle can accumulate dangerous humidity levels within weeks.
Przyspieszenie korozji: Moisture combined with temperature cycling accelerates corrosion of metal components, cable glands, and connection points. This creates a cascade effect where initial corrosion compromises seals, allowing more moisture ingress.
Real-World Impact
I recently worked with Sarah, a facility manager at a water treatment plant in Michigan, who was experiencing frequent failures in her outdoor control panels. The sealed enclosures were rated IP65, but after two years of temperature cycling without proper venting, the internal components showed severe corrosion damage. We installed our breathable vent plugs on the remaining enclosures, and she hasn’t had a single moisture-related failure in over 18 months since the upgrade.
How Do Breathable Vent Plugs Work to Protect Enclosures?
Breathable vent plugs use advanced membrane technology to provide selective permeability, allowing air and gas exchange while maintaining complete protection against liquid water and solid contaminants.
Breathable vent plugs protect enclosures using membrany mikroporowate3 with pore sizes of 0.2-10 microns that allow air molecules to pass through while blocking water droplets that are thousands of times larger. This selective permeability equalizes pressure while maintaining IP65/IP67 protection ratings, preventing condensation and seal damage.
Membrane Technology
Struktura mikroporowata: The heart of a breathable vent plug is its microporous membrane, typically made from expanded PTFE or specialized polymers. These membranes contain billions of microscopic pores that are large enough for air molecules but too small for water droplets to penetrate.
Hydrofobowy4 Właściwości: The membrane surface is treated to be hydrophobic, causing water to bead up and roll off rather than penetrating the pore structure. This ensures that even under pressure, liquid water cannot pass through while maintaining excellent breathability.
Wyrównanie ciśnienia: As temperature changes create pressure differentials, air flows freely through the membrane in both directions, equalizing internal and external pressure instantly. This eliminates the stress on seals and gaskets that causes premature failure.
Protection Mechanisms
Zapobieganie kondensacji: By allowing moisture-laden air to escape and dry air to enter, vent plugs maintain optimal humidity levels inside the enclosure. This prevents the formation of condensation that would otherwise damage sensitive electronics.
Contaminant Filtration: Quality vent plugs incorporate multiple filtration layers that block dust, dirt, and other solid contaminants while maintaining breathability. This is crucial for enclosures in dusty industrial environments.
Odporność chemiczna: Our vent plugs use materials that resist common industrial chemicals, UV radiation, and temperature extremes, ensuring long-term performance in harsh outdoor conditions.
What Types of Vent Plugs Are Best for Different Applications?
Different outdoor applications require specific vent plug designs and materials to ensure optimal performance and longevity in varying environmental conditions.
The best vent plug type depends on environmental conditions, with standard PTFE membranes suitable for most outdoor applications, metal-housed versions for extreme temperatures, and specialized designs for chemical exposure or high-dust environments. Selection criteria include operating temperature range, IP rating requirements, and expected contaminant exposure.
Standard Outdoor Applications
Nylon-Housed Vent Plugs: For typical outdoor enclosures in moderate climates, nylon-housed vent plugs with PTFE membranes provide excellent performance at an economical price point. These handle temperature ranges from -40°C to 85°C and maintain IP65 protection ratings.
Threaded Installation: Most standard applications benefit from threaded vent plugs that provide secure mounting and easy replacement. Common thread sizes include M12x1.5, M16x1.5, and 1/2″ NPT to match standard enclosure knockouts.
UV-Resistant Materials: Outdoor applications require UV-stabilized housing materials to prevent degradation from continuous sun exposure. Our nylon housings include UV inhibitors that maintain structural integrity for over 10 years.
Extreme Environment Applications
Metal-Housed Designs: For extreme temperature applications or corrosive environments, stainless steel or brass-housed vent plugs provide superior durability. These handle temperature ranges from -55°C to 150°C while maintaining chemical resistance.
High-Pressure Ratings: Some applications require vent plugs rated for higher pressure differentials. Our industrial-grade units handle up to 2 bar pressure differential while maintaining breathability and water resistance.
Explosion-Proof Versions: For hazardous locations, we offer Certyfikat ATEX5 explosion-proof vent plugs that meet strict safety requirements while providing essential pressure equalization.
Rozwiązania specyficzne dla aplikacji
| Typ aplikacji | Recommended Vent Plug | Kluczowe cechy | Zakres temperatur |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solar Enclosures | UV-resistant nylon with PTFE | High UV resistance, dust protection | -40°C to 85°C |
| Marine Equipment | Stainless steel housing | Salt spray resistance, IP67 rating | -30°C to 70°C |
| Zakłady chemiczne | PTFE-lined metal housing | Chemical resistance, high pressure | -55°C to 150°C |
| Telekomunikacja | Standard nylon with pre-filter | EMI shielding, easy maintenance | -40°C to 85°C |
How Do You Choose and Install the Right Vent Plug?
Proper selection and installation of vent plugs requires careful consideration of environmental conditions, enclosure specifications, and installation requirements to ensure optimal performance.
Choose the right vent plug by evaluating operating temperature range, IP rating requirements, thread size compatibility, and environmental exposure conditions. Installation requires proper hole preparation, thread sealing, and orientation to prevent direct water exposure while maintaining accessibility for future maintenance.
Kryteria wyboru
Ocena oddziaływania na środowisko: Document the expected operating conditions including temperature range, humidity levels, chemical exposure, and UV radiation. This information determines the required housing material and membrane type.
Enclosure Specifications: Match the vent plug specifications to your enclosure requirements. The vent plug must maintain or exceed the enclosure’s IP rating while providing adequate airflow for the internal volume.
Thread Size and Mounting: Measure existing knockouts or plan new holes to match standard thread sizes. M12x1.5 and M16x1.5 are most common for smaller enclosures, while larger units may use 1/2″ or 3/4″ NPT threads.
Najlepsze praktyki instalacji
Hole Preparation: Use the correct drill bit size for your thread specification. Deburr all holes and clean thoroughly to ensure proper sealing. For metal enclosures, apply anti-seize compound to prevent galling.
Sealing and Torque: Install vent plugs with appropriate O-ring seals or thread sealant. Apply proper torque (typically 15-20 Nm for M16 threads) to ensure sealing without over-stressing the housing.
Optimal Positioning: Mount vent plugs on the side or bottom of enclosures to prevent direct rain exposure. Avoid top mounting unless protected by overhangs or shields. Ensure adequate clearance for future maintenance access.
Weryfikacja jakości
After installation, verify proper function by checking that the membrane moves slightly when gentle pressure is applied to the enclosure. This confirms that pressure equalization is working correctly. Document installation dates and specifications for maintenance scheduling.
What Maintenance Do Vent Plugs Require for Long-Term Performance?
Regular maintenance of vent plugs ensures continued protection and extends both the vent plug life and overall enclosure performance in demanding outdoor environments.
Vent plugs require minimal maintenance consisting of visual inspection every 6 months, cleaning when contaminated, and replacement every 2-5 years depending on environmental conditions. Key maintenance indicators include membrane discoloration, reduced breathability, and physical damage to housing or sealing components.
Inspection Schedule
Routine Visual Checks: Inspect vent plugs every 6 months for obvious damage, contamination, or seal degradation. Look for cracks in the housing, discolored membranes, or accumulation of debris that could block airflow.
Testowanie wydajności: Annually test vent plug function by gently pressing on the enclosure while observing membrane movement. The membrane should flex slightly, indicating proper pressure equalization. Lack of movement suggests blockage or membrane failure.
Monitorowanie środowiska: In harsh environments with high dust, chemical exposure, or extreme temperatures, increase inspection frequency to quarterly. Document any changes in membrane appearance or housing condition.
Cleaning Procedures
Membrane Cleaning: For dust-contaminated membranes, use compressed air to blow debris away from the membrane surface. Never use liquids or solvents that could damage the hydrophobic coating or clog the micropores.
Housing Maintenance: Clean housing surfaces with mild detergent and water, avoiding harsh chemicals that could degrade the material. Ensure all cleaning residue is completely removed before reassembly.
Kontrola uszczelnienia: Check O-ring seals and threads for wear or damage during cleaning. Replace seals if cracked, hardened, or no longer providing proper compression.
Replacement Guidelines
Oczekiwana żywotność: In typical outdoor conditions, quality vent plugs last 3-5 years before replacement. Harsh environments with high contamination, extreme temperatures, or chemical exposure may require replacement every 2-3 years.
Wskaźniki zamienne: Replace vent plugs when membranes show permanent discoloration, reduced flexibility, or visible damage. Any compromise to the housing integrity or sealing capability also requires immediate replacement.
Zapobiegawcza wymiana: Consider preventive replacement during scheduled maintenance outages to avoid unexpected failures. Keep spare vent plugs in inventory for critical applications where downtime must be minimized.
Wnioski
Breathable vent plugs represent one of the most cost-effective investments you can make in outdoor enclosure protection. For less than $10 per enclosure, you can prevent thousands of dollars in equipment damage and eliminate the frustration of premature failures. The key is selecting the right vent plug for your specific application and maintaining it properly over time.
At Bepto, we’ve seen countless customers transform their maintenance programs by implementing proper venting solutions. Our breathable vent plugs have protected enclosures in everything from desert solar installations to offshore marine platforms, consistently delivering years of reliable service.
Don’t wait for the next enclosure failure to convince you of the importance of proper venting. Take action now to protect your investment and ensure reliable operation for years to come. 😉
FAQs About Outdoor Enclosure Vent Plugs
Q: How often should I replace vent plugs on outdoor enclosures?
A: Replace vent plugs every 2-5 years depending on environmental conditions. Harsh environments with high dust, chemicals, or extreme temperatures require more frequent replacement every 2-3 years, while moderate outdoor conditions allow 4-5 year service intervals.
Q: Can I install multiple vent plugs on one enclosure?
A: Yes, larger enclosures often benefit from multiple vent plugs to ensure adequate airflow and pressure equalization. Install one vent plug per 10-20 liters of internal volume, positioning them to avoid direct water exposure while maintaining accessibility.
Q: What’s the difference between IP65 and IP67 rated vent plugs?
A: IP65 vent plugs protect against dust and water jets, suitable for most outdoor applications. IP67 units provide temporary submersion protection up to 1 meter depth, necessary for flood-prone areas or marine applications with wave exposure.
Q: Do vent plugs work in freezing temperatures?
A: Quality vent plugs function effectively in freezing temperatures down to -40°C or lower. The microporous membrane remains flexible and breathable, though airflow rates may decrease slightly. Choose vent plugs with appropriate temperature ratings for your climate.
Q: How do I know if my vent plug is working properly?
A: Test vent plug function by gently pressing on the enclosure while observing the membrane. It should flex slightly, indicating proper pressure equalization. Also check for absence of internal condensation and corrosion, which suggests effective moisture control.
-
Zapoznaj się ze szczegółową tabelą wyjaśniającą system klasyfikacji Ingress Protection (IP) i co oznaczają poszczególne liczby dla odporności na kurz i wodę. ↩
-
Zapoznaj się z pojęciem punktu rosy, czyli temperatury, w której powietrze staje się nasycone parą wodną i zaczyna się kondensacja. ↩
-
Dowiedz się więcej o mikroporowatych membranach i o tym, jak przepuszczają one gaz, blokując jednocześnie ciecze. ↩
-
Explore the principles of hydrophobicity and why certain materials naturally repel water, often described by their contact angle. ↩
-
Zapoznaj się z przeglądem dyrektyw ATEX, przepisów Unii Europejskiej, które określają wymagania dotyczące urządzeń przeznaczonych do użytku w strefach zagrożonych wybuchem. ↩




