Selecting cable glands without understanding applicable standards leads to compliance failures, safety hazards, and costly project delays, while confusion between BS 6121 and EN 62444 requirements causes procurement mistakes, installation problems, and regulatory non-compliance that can result in equipment failures, insurance issues, and legal liability in critical industrial applications. Many engineers struggle with determining which standard applies to their specific project requirements.
BS 6121 and EN 62444 are both European cable gland standards with BS 6121 being the British standard focusing on general industrial applications and EN 62444 being the harmonized European standard1 emphasizing safety and performance requirements, with key differences in testing procedures, dimensional tolerances, material specifications, and certification processes that affect product selection, compliance verification, and international acceptance. Understanding these differences is crucial for proper specification and procurement.
Having worked with procurement managers across manufacturing facilities in Manchester, chemical plants in Rotterdam, and power generation facilities throughout Scandinavia, I’ve learned that understanding cable gland standards is essential for ensuring compliance, safety, and optimal performance. Let me share the critical knowledge for navigating BS 6121 and EN 62444 requirements effectively.
Table of Contents
- What Are the Origins and Scope of BS 6121 and EN 62444 Standards?
- How Do the Technical Requirements Differ Between These Standards?
- What Are the Testing and Certification Differences?
- How Do You Choose the Right Standard for Your Application?
- What Are the Compliance and Documentation Requirements?
- FAQs About Cable Gland Standards
What Are the Origins and Scope of BS 6121 and EN 62444 Standards?
BS 6121 originated as a British standard for cable glands in industrial applications, while EN 62444 was developed as a harmonized European standard to unify cable gland requirements across EU member states, with BS 6121 focusing on traditional British industrial practices and EN 62444 emphasizing modern safety requirements and international harmonization for broader European market acceptance and regulatory compliance.
Understanding the origins and scope helps explain why these standards have different approaches and requirements for cable gland specifications.
BS 6121 Background and Development
Historical Context: BS 6121 was developed by the British Standards Institution (BSI)2 to address specific needs of British industrial applications and traditional manufacturing practices.
Industrial Focus: Emphasizes practical industrial requirements with proven performance in harsh environments including chemical processing, power generation, and heavy manufacturing.
Application Scope: Covers cable glands for general industrial use with specific attention to British electrical installation practices and safety requirements.
Market Acceptance: Widely accepted in UK markets and former British territories with established supply chains and certification processes.
EN 62444 Development and Harmonization
European Harmonization: Developed to create unified European standards that facilitate trade and ensure consistent safety requirements across EU member states.
Safety Emphasis: Places stronger emphasis on safety performance, environmental protection, and user safety compared to traditional industrial standards.
International Alignment: Designed to align with international standards and facilitate global trade while maintaining European safety requirements.
Regulatory Integration: Integrated with European directives and regulations including CE marking3 requirements and product liability frameworks.
Scope and Application Differences
Geographic Coverage: BS 6121 primarily applies to UK markets while EN 62444 covers all European Union member states and associated countries.
Industry Sectors: BS 6121 focuses on traditional industrial sectors while EN 62444 addresses broader applications including commercial, residential, and specialized sectors.
Product Categories: Both standards cover similar product categories but with different emphasis on specific performance characteristics and safety requirements.
Compliance Framework: Different compliance and certification frameworks reflect national versus European regulatory approaches.
Market Impact and Adoption
Supply Chain Effects: Different standards affect supplier qualification, product availability, and certification requirements across European markets.
Cost Implications: Compliance with multiple standards can increase costs but provides broader market access and acceptance.
Technical Innovation: Standards evolution drives technical innovation and improvement in cable gland design and performance.
Future Trends: Ongoing harmonization efforts continue to align standards while maintaining regional requirements and preferences.
David, a procurement manager at a major automotive manufacturing plant in Birmingham, faced confusion when sourcing cable glands for a new production line expansion. The project specifications referenced both BS 6121 and EN 62444 requirements, creating uncertainty about which standard took precedence and what products would ensure compliance. We provided detailed comparison documentation showing how our cable glands meet both standards, along with certification evidence and technical specifications. This clarity enabled confident procurement decisions, ensured regulatory compliance, and avoided costly delays during the facility commissioning process. 😊
How Do the Technical Requirements Differ Between These Standards?
Technical requirements differ significantly between BS 6121 and EN 62444 in areas including dimensional tolerances, material specifications, performance testing, and safety factors, with BS 6121 emphasizing proven industrial performance and EN 62444 focusing on enhanced safety margins and environmental considerations, requiring careful analysis of specific requirements to ensure proper product selection and compliance verification.
Understanding technical differences is crucial because seemingly similar products may not meet both standards without specific design considerations.
Dimensional and Mechanical Requirements
Thread Specifications: BS 6121 primarily uses British Standard Pipe (BSP) threads while EN 62444 accommodates both metric and BSP threading with specific tolerance requirements.
Material Thickness: EN 62444 typically requires greater material thickness for enhanced safety margins compared to BS 6121 minimum requirements.
Mechanical Strength: Different mechanical strength requirements including pull-out forces, compression resistance, and impact resistance specifications.
Dimensional Tolerances: EN 62444 generally has tighter dimensional tolerances to ensure consistent performance across different manufacturers and applications.
Material and Construction Standards
Material Specifications: EN 62444 has more stringent material purity and composition requirements, particularly for metals and polymers used in construction.
Corrosion Resistance: Enhanced corrosion resistance requirements in EN 62444 reflect broader environmental exposure expectations across European climates.
Temperature Ratings: Different temperature rating methodologies and safety factors affect maximum operating temperature specifications.
Chemical Compatibility: EN 62444 includes broader chemical compatibility requirements reflecting diverse European industrial applications.
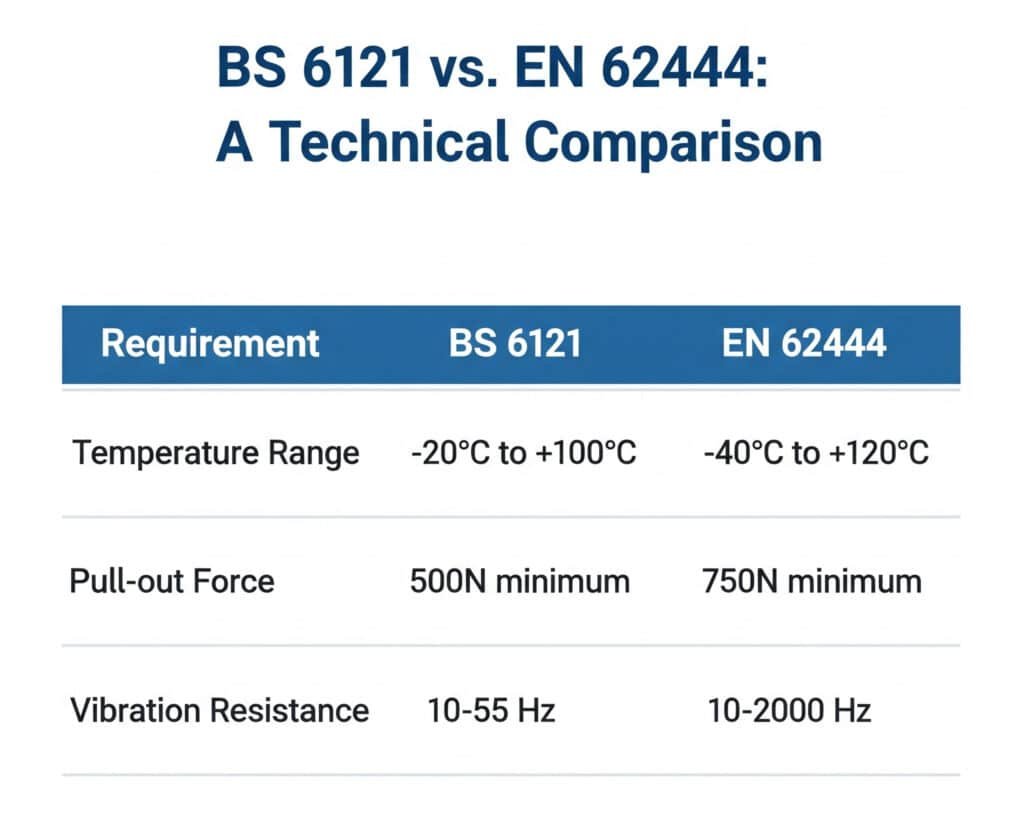
Performance Criteria Comparison
| Requirement Category | BS 6121 | EN 62444 | Key Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| IP Rating Testing4 | IP54-IP68 | IP54-IP68 | Similar ratings, different test procedures |
| Temperature Range | -20°C to +100°C | -40°C to +120°C | EN 62444 has wider range |
| Pull-out Force | 500N minimum | 750N minimum | EN 62444 requires higher strength |
| Vibration Resistance | 10-55 Hz | 10-2000 Hz | EN 62444 covers broader frequency range |
Safety and Environmental Considerations
Safety Factors: EN 62444 incorporates higher safety factors in design calculations to account for diverse application environments and user skill levels.
Environmental Impact: EN 62444 includes environmental impact considerations including material recyclability and manufacturing process requirements.
User Safety: Enhanced user safety requirements in EN 62444 including installation safety, maintenance accessibility, and failure mode analysis.
Regulatory Compliance: Different approaches to regulatory compliance with EN 62444 emphasizing CE marking and product liability requirements.
Quality Assurance Requirements
Manufacturing Standards: EN 62444 requires compliance with ISO 90015 quality management systems while BS 6121 focuses on product performance verification.
Traceability Requirements: Enhanced traceability requirements in EN 62444 for materials, manufacturing processes, and quality control documentation.
Testing Frequency: Different requirements for production testing frequency and statistical quality control procedures.
Documentation Standards: More comprehensive documentation requirements in EN 62444 including technical files and declaration of conformity.
What Are the Testing and Certification Differences?
Testing and certification differences include laboratory accreditation requirements, test procedures, sample sizes, and documentation standards, with BS 6121 using traditional British testing methods and EN 62444 requiring European harmonized testing procedures, affecting certification costs, timeframes, and international acceptance of test results and compliance documentation.
Testing and certification differences directly impact product availability, costs, and regulatory acceptance in different markets.
Laboratory and Accreditation Requirements
Accreditation Bodies: BS 6121 testing requires UKAS-accredited laboratories while EN 62444 accepts any European accreditation body under EA (European Accreditation).
Test Equipment: Different calibration and verification requirements for test equipment affect testing costs and availability.
Personnel Qualifications: Varying requirements for testing personnel qualifications and certification affect laboratory capabilities and costs.
Quality Systems: Different quality system requirements for testing laboratories impact testing reliability and international acceptance.
Test Procedures and Methods
Environmental Testing: EN 62444 includes more comprehensive environmental testing including extended temperature cycling and humidity exposure.
Mechanical Testing: Different mechanical test procedures including tensile strength, compression, and fatigue testing methodologies.
Electrical Testing: Varying electrical testing requirements including insulation resistance, dielectric strength, and continuity testing procedures.
Performance Verification: Different approaches to performance verification including long-term aging tests and accelerated life testing.
Certification Process Differences
Certification Bodies: Different certification bodies and processes affect certification timeframes, costs, and international recognition.
Documentation Requirements: Varying documentation requirements including technical files, test reports, and declaration of conformity formats.
Surveillance Requirements: Different ongoing surveillance and audit requirements for maintaining certification validity.
Mutual Recognition: Limited mutual recognition between standards affects international market access and certification efficiency.
Sample Size and Statistical Requirements
Sample Sizes: EN 62444 typically requires larger sample sizes for statistical validity compared to BS 6121 requirements.
Statistical Methods: Different statistical analysis methods for test result evaluation and acceptance criteria determination.
Batch Testing: Varying requirements for production batch testing and quality control sampling procedures.
Failure Analysis: Different approaches to failure analysis and corrective action requirements for non-conforming products.
Cost and Time Implications
Testing Costs: EN 62444 testing is typically more expensive due to comprehensive requirements and larger sample sizes.
Certification Timeframes: Different certification timeframes affect product launch schedules and market entry timing.
Ongoing Costs: Varying surveillance and maintenance costs for certification validity affect total cost of ownership.
Market Access: Certification under both standards may be required for broad European market access, increasing overall costs.
How Do You Choose the Right Standard for Your Application?
Choosing the right standard depends on project location, regulatory requirements, customer specifications, and market access needs, with BS 6121 being appropriate for UK-focused projects and EN 62444 for broader European applications, requiring analysis of compliance requirements, supply chain considerations, and long-term market strategy to make optimal decisions for specific applications and business objectives.
Standard selection significantly impacts product availability, costs, compliance, and long-term project success.
Geographic and Regulatory Considerations
Project Location: UK projects may specify BS 6121 while continental European projects typically require EN 62444 compliance.
Regulatory Framework: Different regulatory frameworks and enforcement mechanisms affect standard selection and compliance verification.
Local Preferences: Regional preferences and established practices influence standard selection and supplier availability.
Future Expansion: Consider future project expansion and market development when selecting standards for long-term compatibility.
Customer and Specification Requirements
Contract Specifications: Review contract specifications carefully as they may mandate specific standards regardless of geographic location.
End User Preferences: End user preferences and established maintenance practices may influence standard selection decisions.
Insurance Requirements: Insurance companies may have preferences or requirements for specific standards affecting risk assessment and coverage.
Liability Considerations: Different liability frameworks associated with each standard affect risk management and legal considerations.
Supply Chain and Commercial Factors
Supplier Availability: Assess supplier availability and capabilities for each standard in your geographic region and supply chain.
Cost Implications: Compare total costs including product costs, certification, and ongoing compliance requirements.
Delivery Timeframes: Different standards may affect product availability and delivery schedules for critical projects.
Quality Assurance: Evaluate quality assurance capabilities and track records of suppliers for each standard.
Application-Specific Considerations
Environmental Conditions: Harsh environmental conditions may favor one standard over another based on performance requirements.
Safety Criticality: High safety criticality applications may benefit from EN 62444’s enhanced safety requirements and testing procedures.
Maintenance Requirements: Consider maintenance accessibility and procedures when selecting standards for long-term operations.
Upgrade Compatibility: Ensure compatibility with existing installations and future upgrade requirements.
Decision Framework
Requirements Analysis: Systematically analyze all requirements including regulatory, customer, and operational needs.
Risk Assessment: Evaluate risks associated with each standard including compliance, performance, and commercial risks.
Cost-Benefit Analysis: Compare total lifecycle costs and benefits for each standard option.
Implementation Planning: Develop implementation plans including procurement, installation, and ongoing compliance management.
Hassan, who manages operations at a large petrochemical complex in Rotterdam, needed to standardize cable gland specifications across multiple facilities spanning several European countries. The existing mix of BS 6121 and EN 62444 products created maintenance complexity and procurement inefficiencies. We conducted a comprehensive analysis of regulatory requirements, supplier capabilities, and operational needs across all facilities. The recommendation to standardize on EN 62444 provided regulatory compliance across all locations, simplified procurement processes, and reduced maintenance inventory requirements by 40% while ensuring consistent safety performance throughout the complex.
What Are the Compliance and Documentation Requirements?
Compliance and documentation requirements differ significantly between standards, with BS 6121 requiring British conformity assessment and EN 62444 requiring European CE marking and declaration of conformity, including different technical documentation, traceability records, and ongoing compliance monitoring that affect procurement procedures, installation verification, and regulatory audit preparation.
Proper documentation is essential for regulatory compliance, risk management, and successful project completion.
BS 6121 Compliance Framework
British Conformity Assessment: Products must undergo assessment by UKAS-accredited bodies with appropriate technical competence and recognition.
Certificate of Conformity: Manufacturers must provide certificates of conformity demonstrating compliance with all applicable BS 6121 requirements.
Technical Documentation: Comprehensive technical documentation including design specifications, material certificates, and test reports.
Traceability Records: Complete traceability from raw materials through manufacturing to final product delivery and installation.
EN 62444 European Compliance
CE Marking Requirements: Products must bear CE marking indicating conformity with applicable European directives and harmonized standards.
Declaration of Conformity: Manufacturers must provide EU declaration of conformity stating compliance with all applicable requirements.
Technical File: Comprehensive technical file including design documentation, risk assessments, and test reports maintained for regulatory access.
Authorized Representative: Non-EU manufacturers must appoint authorized representatives for regulatory compliance and communication.
Documentation Management
Record Keeping: Different record keeping requirements and retention periods affect document management systems and procedures.
Change Control: Formal change control procedures for modifications affecting compliance status and certification validity.
Audit Preparation: Different audit preparation requirements for regulatory inspections and compliance verification.
Training Records: Personnel training and competency records for installation, maintenance, and inspection activities.
Ongoing Compliance Monitoring
Surveillance Requirements: Different surveillance and monitoring requirements for maintaining certification validity and compliance status.
Performance Monitoring: Ongoing performance monitoring and reporting requirements for critical applications and safety systems.
Corrective Actions: Procedures for corrective actions when non-compliance issues are identified during operations or inspections.
Continuous Improvement: Integration with continuous improvement programs and quality management systems.
International Considerations
Mutual Recognition: Limited mutual recognition between standards affects international project requirements and compliance verification.
Export Requirements: Different export documentation and certification requirements for international projects and shipments.
Local Adaptation: Requirements for local adaptation and additional certifications in specific countries or regions.
Regulatory Updates: Monitoring and implementing regulatory updates and standard revisions affecting ongoing compliance.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between BS 6121 and EN 62444 cable gland standards is essential for proper specification, procurement, and compliance in European markets. While both standards address similar technical requirements, their different approaches to testing, certification, and documentation significantly impact project success.
The key to effective standard selection lies in carefully analyzing project requirements, regulatory frameworks, and commercial considerations to choose the most appropriate standard for your specific application. At Bepto, we provide cable glands that meet both BS 6121 and EN 62444 requirements, along with comprehensive documentation and technical support to ensure your projects achieve optimal compliance and performance.
FAQs About Cable Gland Standards
Q: Can I use BS 6121 cable glands in continental Europe?
A: BS 6121 cable glands may be used in continental Europe if they also meet EN 62444 requirements and have appropriate CE marking. However, check specific country regulations and project specifications to ensure compliance.
Q: What happens to BS 6121 after Brexit?
A: BS 6121 remains valid in the UK market and continues to be recognized by British regulators. However, for EU market access, products typically need EN 62444 compliance and CE marking.
Q: Are EN 62444 cable glands more expensive than BS 6121?
A: EN 62444 cable glands may cost more due to enhanced requirements and testing procedures, but the price difference varies by manufacturer and specific product requirements. Consider total lifecycle costs including compliance and availability.
Q: How do I verify cable gland compliance with these standards?
A: Verify compliance through manufacturer certificates, test reports from accredited laboratories, and appropriate marking (CE for EN 62444). Request complete documentation packages for critical applications.
Q: Can the same cable gland meet both BS 6121 and EN 62444?
A: Yes, many cable glands are designed and tested to meet both standards simultaneously, providing flexibility for projects spanning different markets. Look for dual-certified products from reputable manufacturers.
-
Learn about the role and legal status of harmonised standards within the European Union. ↩
-
Visit the official website of the BSI, the UK’s national standards body. ↩
-
Access the official European Commission guide on CE marking requirements for products. ↩
-
Explore a detailed chart explaining the Ingress Protection (IP) codes and their testing standards. ↩
-
Read an overview of the ISO 9001 standard for quality management systems from the official ISO organization. ↩




