Introduction
As an engineer, you’ve probably faced this challenge: your connector worked perfectly in testing, but failed catastrophically in the field due to seal failure. The difference between dynamic and static sealing can make or break your entire project timeline and budget. Dynamic sealing handles moving parts and vibration, while static sealing provides protection for stationary connections – and choosing the wrong approach costs thousands in redesign and delays. After 10+ years at Bepto Connector, I’ve seen engineers struggle with this fundamental decision, often learning the hard way that not all sealing solutions are created equal.
Table of Contents
- What Are Dynamic and Static Sealing Systems?
- How Do Dynamic Seals Handle Movement and Vibration?
- When Should Engineers Choose Static Sealing Solutions?
- What Are the Key Performance Differences?
- How to Select the Right Sealing Approach?
- FAQ
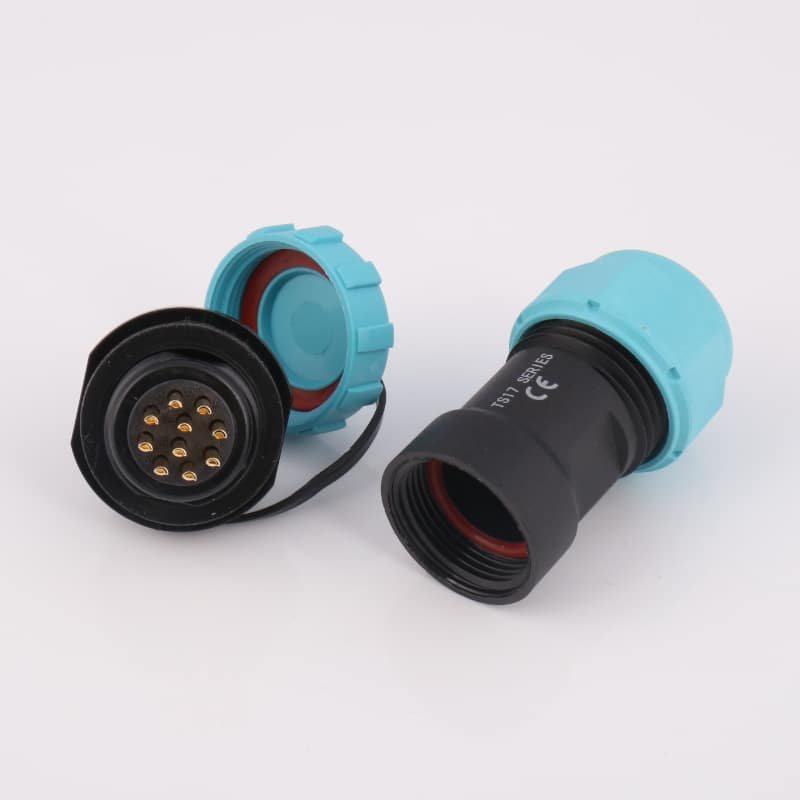
What Are Dynamic and Static Sealing Systems?
Understanding sealing fundamentals can save you months of troubleshooting later. Dynamic sealing systems accommodate relative movement between connector components, while static sealing systems create permanent barriers between stationary parts. The choice impacts everything from material selection to maintenance schedules.

Dynamic Sealing Characteristics
Dynamic seals must maintain their integrity while accommodating:
- Rotational movement up to 360 degrees
- Linear displacement from thermal expansion
- Vibration frequencies from 10Hz to 2000Hz
- Pressure variations during operation
These seals typically use elastomeric materials1 like NBR, EPDM, or specialized compounds that maintain flexibility across temperature ranges. The key challenge lies in balancing seal compression with movement freedom.
Static Sealing Fundamentals
Static seals create permanent barriers through:
- Compression-based sealing using O-rings or gaskets
- Chemical bonding with potting compounds
- Mechanical interference fits2
- Thread-locking compounds for threaded connections
Last month, I worked with David, a procurement manager from a German automotive supplier, who initially specified static seals for a vibrating sensor application. After three prototype failures, we switched to dynamic sealing solutions, reducing his testing time by 6 weeks and saving €15,000 in redesign costs.
How Do Dynamic Seals Handle Movement and Vibration?
Dynamic sealing represents one of the most challenging aspects of connector design. Dynamic seals use flexible materials and specialized geometries to maintain contact pressure while allowing controlled movement, typically achieving IP67-IP68 ratings even under continuous motion.
Movement Accommodation Mechanisms
Dynamic seals handle movement through several key design principles:
Elastic Deformation Control: The seal material stretches and compresses within its elastic limit3, returning to original shape after movement cycles. High-quality silicone and fluoroelastomer compounds can handle over 10 million cycles without degradation.
Pressure Distribution: Advanced dynamic seals distribute contact pressure across multiple contact points, preventing single-point failures that plague simpler designs.
Lubrication Integration: Many dynamic seals incorporate micro-channels or surface treatments that maintain lubrication films, reducing friction and wear during movement.
Real-World Performance Considerations
Temperature cycling presents unique challenges for dynamic seals. At Bepto, we’ve developed specialized compounds that maintain sealing integrity from -40°C to +125°C, crucial for automotive and aerospace applications.
Hassan, who runs a petrochemical facility in Saudi Arabia, recently shared his experience with our dynamic sealing solutions. His rotating equipment connectors previously failed every 6 months due to thermal cycling and vibration. After switching to our specialized dynamic seals, he’s achieved 18 months of continuous operation with zero seal failures, saving his facility $50,000 annually in maintenance costs.
When Should Engineers Choose Static Sealing Solutions?
Static sealing offers superior long-term reliability when movement isn’t a factor. Static seals provide the highest IP ratings (up to IP69K4) and longest service life for stationary applications, often lasting 20+ years without maintenance when properly specified.
Optimal Static Sealing Applications
Static sealing excels in these scenarios:
Permanent Installations: Underground cable connections, building automation systems, and fixed industrial equipment benefit from static sealing’s long-term stability.
High-Pressure Environments: Static seals can handle pressures exceeding 100 bar without the complexity required for dynamic solutions.
Chemical Resistance Requirements: Specialized static seal materials offer superior resistance to aggressive chemicals, acids, and solvents.
Design Considerations for Static Systems
Proper static seal design requires attention to:
- Groove dimensions and surface finish specifications
- Material compatibility with environmental conditions
- Compression ratios for optimal sealing force
- Thermal expansion accommodation through design geometry
The key advantage of static sealing lies in its predictability. Once properly installed, static seals require minimal maintenance and provide consistent performance throughout their service life.
What Are the Key Performance Differences?
Understanding performance trade-offs helps engineers make informed decisions early in the design process. Dynamic seals typically achieve 5-10 year service life with regular maintenance, while static seals can provide 15-25 year maintenance-free operation in suitable applications.
Performance Comparison Matrix
| Parameter | Dynamic Sealing | Static Sealing |
|---|---|---|
| IP Rating | IP67-IP68 | IP68-IP69K |
| Service Life | 5-10 years | 15-25 years |
| Maintenance | Annual inspection | Maintenance-free |
| Cost | Higher initial | Lower initial |
| Temperature Range | -40°C to +125°C | -55°C to +150°C |
| Pressure Rating | Up to 50 bar | Up to 200 bar |
Reliability Factors
Dynamic seals face additional stress factors that static seals avoid:
- Friction-induced wear during movement cycles
- Seal material fatigue from repeated deformation
- Contamination ingress5 during movement phases
- Lubrication degradation over time
However, dynamic seals offer crucial advantages in applications requiring:
- Field serviceability without system shutdown
- Accommodation of thermal expansion in large systems
- Vibration isolation between connector components
- Rotational adjustment during installation
How to Select the Right Sealing Approach?
Sealing selection impacts your entire project timeline and budget. Choose dynamic sealing when your application involves movement, vibration, or thermal cycling; select static sealing for permanent installations requiring maximum reliability and minimal maintenance.
Decision Framework
Follow this systematic approach for sealing selection:
Step 1: Movement Analysis
- Document all potential movement sources (thermal, mechanical, vibrational)
- Quantify movement ranges and frequencies
- Identify critical seal locations
Step 2: Environmental Assessment
- Temperature range requirements
- Chemical exposure conditions
- Pressure and vacuum specifications
- IP rating requirements
Step 3: Lifecycle Considerations
- Required service life
- Maintenance accessibility
- Replacement cost implications
- System downtime tolerance
Implementation Best Practices
Successful sealing implementation requires:
Material Selection: Choose seal materials based on worst-case environmental conditions, not typical operating parameters.
Installation Procedures: Develop detailed installation procedures to prevent seal damage during assembly.
Quality Control: Implement seal integrity testing before system deployment.
Maintenance Planning: Establish inspection schedules based on seal type and operating conditions.
Conclusion
The choice between dynamic and static sealing fundamentally shapes your connector’s performance, reliability, and lifecycle costs. Dynamic sealing solutions excel in applications requiring movement accommodation and field serviceability, while static sealing provides unmatched long-term reliability for permanent installations. At Bepto Connector, we’ve helped thousands of engineers navigate this critical decision, combining our manufacturing expertise with real-world application knowledge to deliver optimal sealing solutions. Remember: the right sealing choice made early saves exponentially more than any optimization attempted later in your project timeline.
FAQ
Q: What is the main difference between dynamic and static sealing in connectors?
A: Dynamic sealing accommodates movement and vibration while maintaining seal integrity, while static sealing creates permanent barriers for stationary connections. Dynamic seals use flexible materials and specialized geometries, whereas static seals rely on compression and permanent installation.
Q: How long do dynamic seals typically last compared to static seals?
A: Dynamic seals typically provide 5-10 years of service life with regular maintenance, while static seals can operate maintenance-free for 15-25 years. The difference stems from wear factors like friction and repeated deformation in dynamic applications.
Q: Can I use static sealing in applications with slight movement or vibration?
A: Static seals can handle minimal thermal expansion but will fail under continuous vibration or movement. If your application experiences regular movement exceeding 0.5mm or vibration above 10Hz, dynamic sealing solutions are recommended to prevent premature failure.
Q: Which sealing type offers better IP ratings for harsh environments?
A: Static sealing typically achieves higher IP ratings (up to IP69K) due to permanent compression and no movement-related seal compromise. Dynamic sealing usually reaches IP67-IP68 ratings, which still provide excellent protection for most industrial applications.
Q: How do I calculate the cost difference between dynamic and static sealing solutions?
A: Consider total lifecycle costs including initial seal cost, installation complexity, maintenance requirements, and replacement frequency. While dynamic seals cost 2-3x more initially, static seals may require complete system disassembly for replacement, making dynamic solutions more cost-effective for serviceable applications.
-
Learn about elastomers, the class of polymers known for their viscosity and elasticity. ↩
-
Explore the mechanical engineering principle of an interference fit, where parts are joined by friction after insertion. ↩
-
Understand the concept of the elastic limit, the maximum stress a material can withstand before permanent deformation. ↩
-
Discover the specifics of the IP69K rating, which designates protection against high-pressure, high-temperature water jets. ↩
-
Learn how contamination ingress, the entry of foreign particles, can cause premature failure in sealed systems. ↩