Choosing the wrong threading system for your cable glands can lead to installation nightmares, costly delays, and even safety hazards. With three major threading standards dominating the global market, engineers and procurement managers often struggle to make the right choice for their specific applications.
The answer is straightforward: PG threads1 excel in European industrial applications, Metric threads2 offer the best versatility for international projects, while NPT threads3 remain the gold standard for North American installations. Each system has distinct advantages depending on your geographical location, industry requirements, and equipment compatibility.
As someone who’s helped countless clients navigate this decision over the past decade, I’ve seen how the wrong choice can turn a simple installation into a expensive headache. Let me share the insights that will save you time, money, and frustration.
Table of Contents
- What Are the Key Differences Between PG, Metric, and NPT Threads?
- When Should You Choose PG Threading Systems?
- Why Are Metric Threads Becoming the Global Standard?
- Where Do NPT Threads Still Dominate the Market?
- How Do You Select the Right Threading System for Your Project?
- FAQs About Cable Gland Threading Systems
What Are the Key Differences Between PG, Metric, and NPT Threads?
Understanding these three threading systems is crucial for any successful cable gland installation project.
The fundamental differences lie in their design philosophy, measurement systems, and sealing mechanisms. PG (Panzer-Gewinde) threads use a German standard with coarse pitch, Metric threads follow ISO standards with fine pitch options, while NPT (National Pipe Thread) features a tapered design4 for self-sealing.
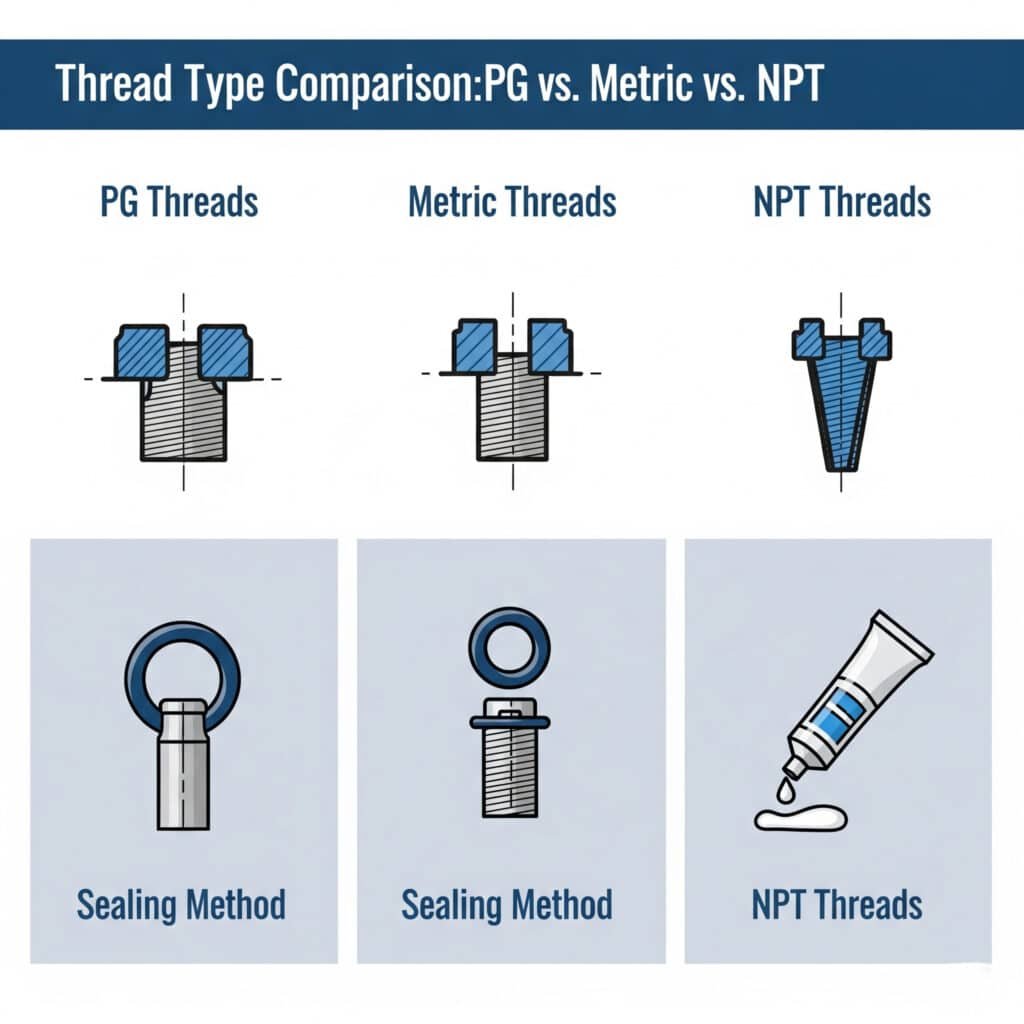
Technical Specifications Breakdown
| Feature | PG Threads | Metric Threads | NPT Threads |
|---|---|---|---|
| Origin | German DIN 40430 | ISO 262 Standard | American ANSI/ASME |
| Thread Type | Straight/Parallel | Straight/Parallel | Tapered (1:16) |
| Pitch | Coarse (1.5-2.0mm) | Fine/Coarse Options | Variable by Size |
| Sealing Method | O-ring/Gasket | O-ring/Gasket | Thread Compound |
| Size Range | PG7 to PG48 | M12 to M75+ | 1/8″ to 4″+ |
Last month, I worked with David, a procurement manager from a major automotive manufacturer in Detroit. He was frustrated because his European equipment required PG threading, but his local suppliers only stocked NPT variants. This mismatch cost his project three weeks and significant budget overruns – a perfect example of why understanding these differences matters.
Manufacturing and Quality Considerations
From our production perspective at Bepto, each threading system demands different tooling and quality control processes. PG threads require precise German-standard tooling, while NPT threads need specialized tapered cutting equipment. This directly impacts lead times and pricing, especially for custom specifications.
When Should You Choose PG Threading Systems?
PG threading remains the preferred choice for specific industrial applications, particularly in European markets.
Choose PG threads when working with German or European machinery, legacy industrial systems, or applications requiring robust mechanical connections. The coarse pitch design provides excellent mechanical strength and is less susceptible to cross-threading5 during installation.
Industrial Applications Where PG Excels
PG threading systems shine in heavy industrial environments. The robust design handles high vibration and mechanical stress better than finer thread alternatives. I’ve seen PG cable glands perform flawlessly in steel mills, chemical plants, and automotive assembly lines where other threading systems failed.
The standardized sizing also simplifies inventory management. Unlike NPT’s fractional sizing, PG uses logical numerical progression (PG7, PG9, PG11, etc.), making specification and ordering more intuitive for technical teams.
Geographic and Market Considerations
European markets, particularly Germany, Austria, and Switzerland, heavily favor PG threading. If you’re supplying equipment or services to these regions, PG compatibility often becomes a mandatory requirement rather than an option.
However, I’ve noticed a gradual shift toward Metric threading even in traditional PG markets, driven by globalization and cost optimization initiatives.
Why Are Metric Threads Becoming the Global Standard?
Metric threading systems are rapidly gaining market share worldwide due to their versatility and international standardization.
Metric threads offer the best balance of global compatibility, size variety, and manufacturing efficiency. Following ISO standards, they provide consistent specifications across different manufacturers and countries, reducing procurement complexity for international projects.
Advantages of Metric Threading
The metric system’s decimal-based sizing eliminates confusion common with fractional systems. M20 x 1.5 clearly indicates a 20mm diameter with 1.5mm pitch – no conversion calculations needed. This clarity reduces specification errors and improves project efficiency.
From a manufacturing standpoint, metric tooling is widely available and cost-effective. Most modern CNC equipment defaults to metric programming, making production more efficient and economical.
International Project Success Story
Hassan, who manages a large petrochemical facility in Saudi Arabia, recently shared his experience with metric threading standardization. His multinational project team included suppliers from Germany, Japan, and the US. By standardizing on metric cable glands, they eliminated compatibility issues and reduced inventory complexity by 40%.
The project completed two weeks ahead of schedule, primarily due to the simplified procurement and installation process that metric standardization enabled.
Where Do NPT Threads Still Dominate the Market?
NPT threading maintains strong market position in North America and specific industrial applications.
NPT threads excel in North American installations, oil and gas applications, and systems requiring self-sealing thread connections. The tapered design creates metal-to-metal sealing without additional gaskets, making it ideal for high-pressure applications.
North American Market Dynamics
The established infrastructure in the United States and Canada heavily favors NPT threading. Electrical codes, industry standards, and technician training all center around NPT specifications. Changing this entrenched system would require massive industry coordination and retraining efforts.
NPT’s fractional sizing (1/2″, 3/4″, 1″, etc.) aligns with traditional American measurement systems, making it intuitive for local workforce and existing inventory systems.
Technical Advantages in Specific Applications
The tapered design of NPT threads provides unique advantages in certain applications. The interference fit creates excellent sealing properties, particularly valuable in pneumatic and hydraulic systems where leak prevention is critical.
However, this same tapered design can create installation challenges. Over-tightening can crack housings, while under-tightening leads to leaks. Proper installation requires more skill and experience compared to straight thread alternatives.
How Do You Select the Right Threading System for Your Project?
Selecting the optimal threading system requires careful consideration of multiple factors beyond simple technical specifications.
Base your decision on equipment compatibility, geographic requirements, supply chain capabilities, and long-term maintenance considerations. The “best” technical solution isn’t always the most practical choice for your specific situation.
Decision Matrix Framework
| Priority Factor | PG Best Choice | Metric Best Choice | NPT Best Choice |
|---|---|---|---|
| Geographic Focus | Europe/Germany | Global/International | North America |
| Equipment Base | European Machinery | Mixed International | American Equipment |
| Supply Chain | European Suppliers | Global Suppliers | North American |
| Technician Skills | European Training | International | American Training |
| Future Expansion | European Markets | Global Markets | North American |
Practical Implementation Strategy
Start by auditing your existing equipment and infrastructure. Document current threading systems, supplier capabilities, and technician expertise. This baseline assessment reveals compatibility requirements and potential conversion costs.
Consider your expansion plans. If you’re planning international growth, metric threading offers the most flexibility. For regional focus, stick with your market’s dominant standard to minimize complexity and costs.
Supply Chain and Inventory Optimization
From our experience at Bepto, mixed threading systems significantly increase inventory costs and complexity. Standardizing on one system, where possible, reduces SKU count, simplifies procurement, and improves economies of scale.
However, forced standardization can create compatibility issues with existing equipment. Balance standardization benefits against retrofit costs and operational disruption.
Conclusion
The choice between PG, Metric, and NPT threading systems ultimately depends on your specific application requirements, geographic focus, and existing infrastructure. PG threads serve European industrial applications well, Metric threads provide the best global compatibility, while NPT remains essential for North American markets.
Success comes from matching your threading choice to your operational reality rather than chasing theoretical advantages. Consider your equipment base, supply chain capabilities, technician expertise, and future expansion plans when making this critical decision.
At Bepto, we maintain comprehensive inventory across all three threading systems because we understand that one size doesn’t fit all applications. Whether you need PG robustness, Metric versatility, or NPT compatibility, the right choice is the one that serves your specific operational needs most effectively.
FAQs About Cable Gland Threading Systems
Q: Can I convert between PG, Metric, and NPT threading systems?
A: Direct conversion isn’t possible due to different thread pitches and diameters. You’ll need adapters or complete component replacement. Adapters work for low-stress applications but may compromise sealing integrity in demanding environments.
Q: Which threading system offers the best sealing performance?
A: NPT threads provide excellent sealing through their tapered design, while PG and Metric systems rely on gaskets or O-rings. Properly installed, all three systems achieve IP68 ratings, but NPT requires more installation expertise.
Q: Are metric cable glands more expensive than PG or NPT alternatives?
A: Pricing varies by region and volume. Metric glands often cost less in international markets due to higher production volumes, while PG and NPT may be more economical in their respective regional markets.
Q: How do I identify which threading system my existing equipment uses?
A: Measure the thread diameter and pitch using thread gauges. PG uses specific sizes (PG7=12.5mm, PG9=15.2mm), Metric follows standard diameters (M20, M25, M32), while NPT uses fractional inches with tapered threads.
Q: Can I mix different threading systems in the same installation?
A: While technically possible with adapters, mixing systems increases complexity, potential failure points, and maintenance requirements. Standardizing on one system per installation zone is recommended for optimal performance and serviceability.
-
Learn about the German DIN 40430 standard that specifies the dimensions for Panzer-Gewinde (PG) threads. ↩
-
Explore the international standards for general-purpose metric screw threads, the most commonly used type worldwide. ↩
-
Review the American National Standard for tapered pipe threads used for sealing and joining pipes and fittings. ↩
-
Understand the mechanical principle behind tapered threads and how they create a seal through an interference fit. ↩
-
Learn about this common installation error and discover techniques to ensure proper thread alignment. ↩



