Introduction
Ever wondered why some waterproof connectors fail after just months of outdoor exposure while others last decades in harsh marine environments? The secret lies in choosing the right sealing mechanism – a decision that can make or break your entire electrical system. O-rings provide dynamic sealing1 for removable connections, gaskets offer cost-effective static sealing for permanent installations, while potting delivers the ultimate protection through complete encapsulation, each serving specific applications based on environmental demands and maintenance requirements.
Just last week, Marcus from a solar installation company in Phoenix called me in frustration. His team had installed 500 solar panel junction boxes with basic gasket sealing, confident they’d chosen the right solution. After Arizona’s monsoon season, 30% of the connections had failed due to water ingress, causing $150,000 in damage and threatening their reputation with a major utility client.
Table of Contents
- What Are the Three Main Sealing Methods for Waterproof Connectors?
- How Do O-Ring Seals Work in Waterproof Connectors?
- When Should You Choose Gasket Sealing Solutions?
- Why Is Potting the Ultimate Sealing Method?
- How to Select the Right Sealing Method for Your Application?
- FAQs About Waterproof Connector Sealing
What Are the Three Main Sealing Methods for Waterproof Connectors?
Understanding the fundamental differences between sealing mechanisms is crucial for any engineer or procurement manager dealing with waterproof connectors. Each method offers distinct advantages and limitations that directly impact performance, cost, and maintenance requirements.
The three primary sealing methods are O-ring seals for dynamic applications requiring regular access, gasket seals for static installations prioritizing cost-effectiveness, and potting compounds for permanent protection in extreme environments.
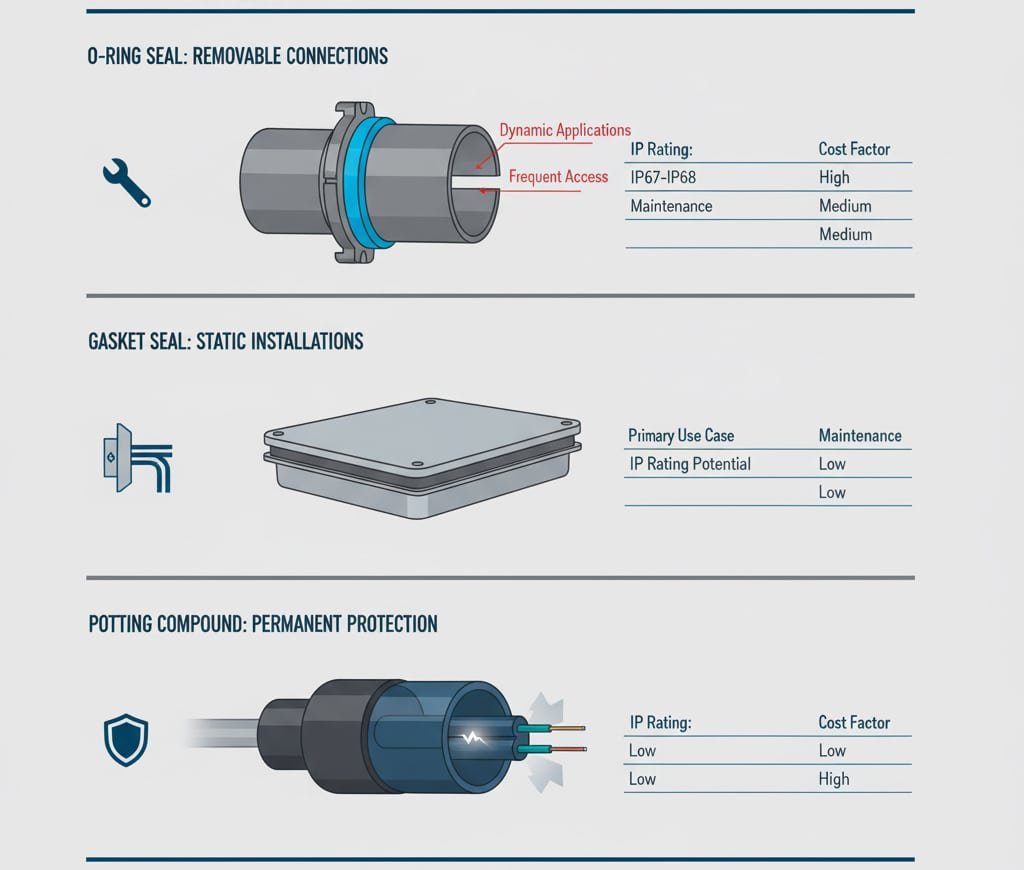
Sealing Method Comparison Overview
| Sealing Method | Primary Use Case | IP Rating Potential | Maintenance Level | Cost Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O-Ring | Removable connections | IP67-IP68 | High (periodic replacement) | Medium |
| Gasket | Static installations | IP65-IP67 | Low (inspect annually) | Low |
| Potting | Permanent protection | IP68-IP69K | None (permanent seal) | High |
Key Performance Factors
The effectiveness of any sealing method depends on several critical factors:
Environmental Conditions: Temperature cycling, chemical exposure, and UV radiation all affect seal longevity. O-rings excel in temperature extremes but require material compatibility checks. Gaskets offer broad chemical resistance but may degrade under UV exposure. Potting provides comprehensive protection but requires careful material selection for thermal expansion compatibility.
Application Requirements: Dynamic applications requiring frequent access favor O-ring solutions, while permanent installations benefit from potting. Gaskets serve well in semi-permanent applications where occasional access is needed.
Regulatory Compliance: Different industries mandate specific sealing standards. Marine applications often require potted solutions for critical systems, while automotive applications may accept O-ring sealing for serviceable components.
How Do O-Ring Seals Work in Waterproof Connectors?
O-ring sealing represents the most versatile approach to waterproof connector design, offering reliable protection while maintaining serviceability – a critical factor in many industrial applications.
O-ring seals create waterproof barriers through controlled compression of elastomeric rings within precisely machined grooves, providing reliable sealing while allowing repeated connection and disconnection cycles.
O-Ring Sealing Mechanics
The science behind O-ring sealing relies on controlled deformation. When properly installed, the O-ring compresses by 15-25% of its cross-sectional diameter, creating intimate contact with both the groove walls and the mating surface. This compression generates the sealing force while maintaining elasticity for repeated use.
Material Selection Considerations:
- Nitrile (NBR): General purpose, -40°C to +100°C, excellent oil resistance
- Viton (FKM): High temperature, -20°C to +200°C, superior chemical resistance
- EPDM: Weather resistance, -50°C to +150°C, excellent ozone resistance
- Silicone: Food grade applications, -60°C to +200°C, FDA compliant options
Real-World Application Example
I remember working with Ahmed, an engineering manager at a petrochemical facility in Kuwait. His team needed waterproof connectors for instrumentation in a high-temperature, chemically aggressive environment. Standard NBR O-rings were failing within months due to hydrogen sulfide exposure.
We switched to Viton O-rings with custom groove designs optimized for thermal expansion. The result? Three years of operation without a single seal failure, saving his facility over $300,000 in unplanned maintenance and production losses.
O-Ring Installation Best Practices
Proper installation is critical for O-ring success:
- Groove Design: Follow AS568 or ISO 3601 standards2 for groove dimensions
- Surface Finish: Maintain 16-32 RMS surface finish on sealing surfaces
- Installation Tools: Use proper installation tools to prevent nicking or twisting
- Lubrication: Apply compatible lubricant to ease installation and improve sealing
When Should You Choose Gasket Sealing Solutions?
Gasket sealing offers an economical approach to waterproof connector design, particularly suited for applications where cost optimization and simple installation are priorities.
Gasket sealing provides effective water protection through flat or formed elastomeric sheets that compress between mating surfaces, offering cost-effective solutions for static applications with moderate environmental exposure.
Gasket Types and Applications
Flat Gaskets: Simple die-cut sheets ideal for large, flat sealing surfaces. Common in junction boxes and panel-mount connectors where space allows for wide sealing surfaces.
Formed Gaskets: Molded or extruded profiles that follow complex connector geometries. These provide better sealing in confined spaces but require custom tooling.
Adhesive-Backed Gaskets: Pre-applied adhesive eliminates installation errors and ensures proper positioning. Popular in high-volume assembly operations.
Material Options and Selection
| Material | Temperature Range | Key Benefits | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neoprene | -40°C to +100°C | Weather resistance, flame retardant | Outdoor enclosures |
| Silicone Foam | -55°C to +200°C | Compression set resistance | High-temperature applications |
| EPDM | -50°C to +150°C | Ozone resistance, longevity | Automotive, marine |
| Polyurethane | -30°C to +80°C | Abrasion resistance, flexibility | Industrial equipment |
Gasket Sealing Limitations
While cost-effective, gasket sealing has inherent limitations:
Compression Set3: Over time, gaskets lose their ability to maintain sealing force, particularly under constant compression and temperature cycling.
Installation Sensitivity: Uneven compression can create leak paths. Proper torque specifications and sequence are critical.
Limited Reusability: Most gaskets are single-use items, making maintenance more expensive than O-ring solutions.
Why Is Potting the Ultimate Sealing Method?
For applications demanding absolute waterproof integrity, potting compounds provide unmatched protection by completely encapsulating vulnerable connection points.
Potting creates permanent waterproof seals by filling connector cavities with liquid compounds that cure into solid, impermeable barriers, eliminating all potential leak paths while providing mechanical strain relief.
Potting Compound Categories
Epoxy Compounds: Excellent adhesion and chemical resistance, ideal for permanent installations. Cure at room temperature or with heat acceleration. Shore hardness4 typically 70D-85D.
Polyurethane Compounds: Superior flexibility and impact resistance. Better thermal cycling performance than epoxy. Shore hardness range 30A-70D allows stress accommodation.
Silicone Compounds: Outstanding temperature range (-65°C to +200°C) and UV resistance. Lower mechanical strength but excellent for outdoor applications requiring flexibility.
Advanced Potting Techniques
Vacuum Potting5: Eliminates air bubbles that could create leak paths. Essential for critical applications requiring 100% void-free encapsulation.
Two-Stage Potting: Initial seal with fast-cure compound followed by full encapsulation. Reduces processing time while ensuring complete protection.
Selective Potting: Protects only critical areas while maintaining access to serviceable components. Requires precise masking and application control.
Performance Advantages
Potting offers several unique benefits:
- Complete Environmental Isolation: No leak paths exist once properly cured
- Mechanical Protection: Encapsulation provides impact and vibration resistance
- Strain Relief: Gradual stiffness transition reduces cable stress concentration
- Corrosion Prevention: Eliminates moisture and oxygen access to metal components
Industry-Specific Requirements
Different industries have developed specialized potting standards:
Aerospace: AS9100 quality requirements, flame-retardant compounds, outgassing specifications
Marine: DNV GL approval, saltwater immersion testing, UV resistance validation
Automotive: IATF 16949 compliance, thermal cycling requirements, chemical compatibility testing
How to Select the Right Sealing Method for Your Application?
Choosing the optimal sealing method requires systematic evaluation of environmental conditions, performance requirements, and lifecycle costs.
Sealing method selection depends on balancing environmental protection requirements, maintenance accessibility needs, cost constraints, and regulatory compliance standards specific to your application.
Decision Matrix Framework
| Factor | O-Ring Priority | Gasket Priority | Potting Priority |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serviceability | High | Medium | None |
| Environmental Severity | Medium | Low | High |
| Initial Cost | Medium | Low | High |
| Lifecycle Cost | Medium | High | Low |
| Installation Complexity | Medium | Low | High |
Environmental Assessment Checklist
Temperature Considerations:
- Operating range: Continuous vs. intermittent exposure
- Thermal cycling: Frequency and magnitude of temperature changes
- Thermal shock: Rapid temperature transitions
Chemical Exposure:
- Cleaning agents: Frequency and concentration
- Process chemicals: Direct contact vs. vapor exposure
- Fuel compatibility: Gasoline, diesel, hydraulic fluids
Mechanical Stress:
- Vibration levels: Frequency and amplitude
- Impact resistance: Drop test requirements
- Flexing cycles: Cable movement expectations
Cost Analysis Framework
Initial Costs:
- Material costs per unit
- Tooling and equipment requirements
- Labor and processing time
- Quality control and testing
Lifecycle Costs:
- Maintenance frequency and complexity
- Replacement part availability
- Downtime costs during service
- End-of-life disposal considerations
Regulatory Compliance Matrix
Different applications require specific certifications:
Marine Applications: IP68 minimum, salt spray testing (ASTM B117), UV resistance (ASTM G154)
Automotive: IP67 standard, thermal cycling (IEC 60068), vibration resistance (ISO 16750)
Industrial: IP65-IP67 typical, chemical compatibility testing, flame retardancy (UL94)
Conclusion
The choice between O-ring, gasket, and potting sealing methods ultimately determines the long-term reliability and cost-effectiveness of your waterproof connector system. O-rings excel where serviceability matters, gaskets provide economical solutions for moderate environments, and potting delivers uncompromising protection for critical applications. At Bepto Connector, we’ve seen how the right sealing choice can transform project outcomes – from preventing costly failures to enabling new applications in extreme environments. The key is matching the sealing technology to your specific requirements rather than defaulting to the lowest-cost option. Remember, the most expensive seal is the one that fails when you need it most! 😉
FAQs About Waterproof Connector Sealing
Q: How long do O-rings last in waterproof connectors?
A: O-ring lifespan typically ranges from 2-10 years depending on material, environment, and usage frequency. Viton O-rings in moderate conditions often exceed 5 years, while NBR in harsh chemicals may require annual replacement. Regular inspection and proper installation significantly extend service life.
Q: Can I reuse gaskets when servicing waterproof connectors?
A: Most gaskets are single-use components that lose sealing effectiveness after compression. Reusing gaskets risks water ingress and system failure. Only specially designed reusable gaskets with minimal compression set should be considered for multiple installations, and only after careful inspection.
Q: What’s the difference between IP67 and IP68 ratings for potted connectors?
A: IP67 protects against temporary water immersion up to 1 meter for 30 minutes, while IP68 provides protection during continuous submersion at depths specified by the manufacturer. Potted connectors can achieve either rating depending on compound selection and application technique.
Q: How do I prevent air bubbles when potting waterproof connectors?
A: Use vacuum potting equipment to remove air before compound curing, select low-viscosity compounds that flow easily around components, and apply potting in multiple thin layers rather than single thick pours. Proper degassing of the compound before application is also critical.
Q: Which sealing method works best for high-temperature applications?
A: For temperatures above 150°C, silicone O-rings or high-temperature potting compounds perform best. Gaskets typically have lower temperature limits. Viton O-rings handle up to 200°C, while specialized silicone potting compounds can withstand 250°C+ continuously.
-
Learn the key differences between dynamic seals, used for moving parts, and static seals for fixed components. ↩
-
Review the official industry standards like AS568 that define uniform sizing for O-rings. ↩
-
Understand the material property of compression set and how it affects the long-term performance of a seal. ↩
-
Explore the Shore hardness scale and how it is used to measure the indentation hardness of polymers and elastomers. ↩
-
Discover the benefits of the vacuum potting technique for creating void-free, highly reliable electronic encapsulations. ↩


