Introduction
Staring at a cable gland specification sheet with M20x1.5 and PG16 options, feeling completely lost about which threading system to choose? You’re facing one of the most fundamental yet confusing decisions in cable management. The wrong choice could lead to installation nightmares, seal failures, or compatibility issues that cost thousands in rework.
M-type threads (metric ISO standard) offer finer pitch and better sealing characteristics, while PG-type threads (German DIN standard) provide coarser pitch for faster installation – the choice depends on your specific application requirements including sealing performance, installation speed, and regional preferences.
Just last week, David, a project manager from a manufacturing facility in Ohio, called us frantically after discovering his entire cable gland order used PG threads while his equipment panels were tapped for M-type threads. This costly mistake could have been avoided with proper understanding of these threading systems. Let me break down everything you need to know to make the right choice every time.
Table of Contents
- What Are the Fundamental Differences Between M-Type and PG-Type Threads?
- Which Threading System Offers Better Sealing Performance?
- How Do Installation Requirements Compare Between Both Systems?
- What Are the Regional and Industry Preferences?
- Which System Should You Choose for Specific Applications?
- FAQs About M-Type vs PG-Type Cable Gland Threads
What Are the Fundamental Differences Between M-Type and PG-Type Threads?
Confused by the technical specifications? Let me simplify the core differences that actually matter for your applications.
M-type threads follow ISO metric standards with finer thread pitch (typically 1.5mm), while PG-type threads use German DIN standards with coarser pitch (varies by size), resulting in different sealing characteristics, installation torque requirements, and compatibility with international equipment.
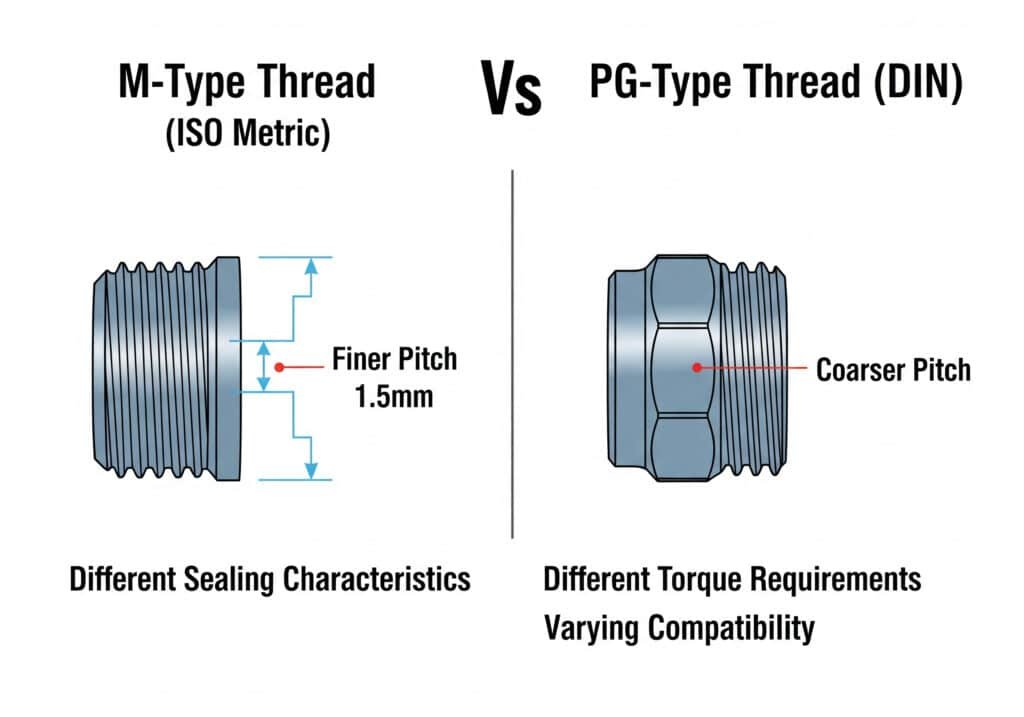
Technical Specifications Comparison
M-Type Thread Characteristics:
- Standard: ISO 262 metric thread1
- Thread angle: 60 degrees
- Pitch: Consistent (1.5mm for most cable gland sizes)
- Profile: Sharp V-thread with flat crest and root
- Designation: M20x1.5, M25x1.5, M32x1.5
PG-Type Thread Characteristics:
- Standard: DIN 404302 (German industrial standard)
- Thread angle: 55 degrees
- Pitch: Variable by size (PG7=0.75mm, PG16=1.5mm, PG21=1.5mm)
- Profile: Rounded thread form
- Designation: PG7, PG9, PG11, PG13.5, PG16, PG21, PG29, PG36, PG42, PG48
Historical Development Context
Understanding the origins helps explain current usage patterns:
M-Type Evolution:
- Developed as part of ISO standardization efforts
- Designed for global compatibility
- Optimized for precision manufacturing
- Widely adopted in modern equipment design
PG-Type Heritage:
- Originally developed in Germany for industrial applications
- “PG” stands for “Panzer-Gewinde3” (armor thread)
- Established in electrical panel and enclosure industry
- Strong presence in European industrial equipment
Hassan, who manages a chemical processing facility in Dubai, shared an interesting perspective: “We initially preferred PG threads because our German equipment suppliers used them exclusively. However, as we expanded globally and sourced from various manufacturers, M-type threads became more practical for standardization.”
Size and Cable Compatibility
| M-Type Size | Cable Range (mm) | PG-Type Equivalent | Cable Range (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| M12x1.5 | 3-6.5 | PG7 | 3-6.5 |
| M16x1.5 | 4-10 | PG9 | 4-8 |
| M20x1.5 | 6-12 | PG13.5 | 6-12 |
| M25x1.5 | 13-18 | PG16 | 10-14 |
| M32x1.5 | 15-25 | PG21 | 13-18 |
Notice how the cable ranges don’t always align perfectly – this is where selection becomes critical for optimal performance.
Which Threading System Offers Better Sealing Performance?
When it comes to maintaining IP ratings and preventing ingress, thread design plays a crucial role that many engineers overlook.
M-type threads generally provide superior sealing performance due to their finer pitch and consistent thread geometry, creating more contact points and better compression of sealing elements, while PG-type threads rely more heavily on O-ring seals for ingress protection.
Sealing Mechanism Analysis
M-Type Sealing Advantages:
- Finer thread pitch creates more sealing surfaces per unit length
- Consistent 1.5mm pitch allows standardized seal design
- Sharp thread profile provides better metal-to-metal contact
- Higher thread engagement per turn improves seal integrity
PG-Type Sealing Characteristics:
- Variable pitch requires size-specific seal optimization
- Rounded thread profile may create slight gaps
- Coarser threads provide fewer sealing contact points
- Relies heavily on O-ring compression for primary seal
Real-World Sealing Performance
David’s Ohio facility provided an excellent case study. They were experiencing intermittent IP rating failures with their existing PG-threaded cable glands in a washdown environment4. After switching to M-type threads with our enhanced sealing design, they achieved:
- Consistent IP68 performance under high-pressure washdown
- Reduced maintenance intervals due to better seal longevity
- Improved reliability in temperature cycling conditions
- Lower total cost of ownership through reduced seal replacements
Environmental Impact on Sealing
Temperature Cycling Effects:
- M-type threads maintain better seal integrity during expansion/contraction
- Finer pitch distributes thermal stress more evenly
- PG threads may experience seal extrusion under extreme conditions
Chemical Resistance:
- Both systems perform similarly with proper seal material selection
- M-type threads offer slightly better seal retention under chemical attack
- Thread compound compatibility remains crucial for both systems
Vibration Resistance:
- M-type threads resist loosening better due to finer pitch
- PG threads may require thread locking compounds in high-vibration applications
- Both benefit from proper installation torque
At Bepto, we’ve conducted extensive testing comparing both systems under various environmental conditions. Our M-type cable glands consistently demonstrate 15-20% better long-term seal retention in accelerated aging tests5.
How Do Installation Requirements Compare Between Both Systems?
Installation efficiency can significantly impact project timelines and labor costs – here’s what you need to know about practical differences.
PG-type threads install faster due to coarser pitch requiring fewer turns, while M-type threads demand more precision but offer better control over seal compression and final positioning, making installation method selection dependent on project priorities and technician skill levels.
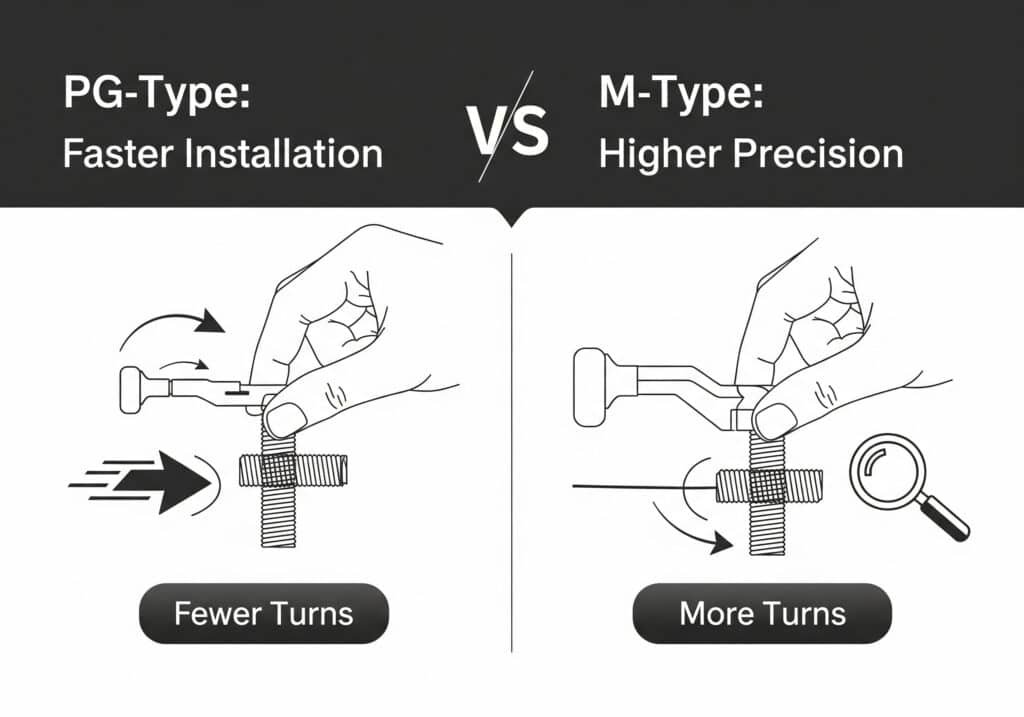
Installation Speed Analysis
PG-Type Installation Advantages:
- Fewer turns required – typically 3-4 full turns for engagement
- Faster threading reduces installation time per gland
- Less precise torque control needed for basic applications
- Forgiving installation for less experienced technicians
M-Type Installation Characteristics:
- More turns required – typically 6-8 full turns for full engagement
- Precise torque control essential for optimal sealing
- Better final positioning control due to finer adjustment capability
- Requires more skilled installation for optimal performance
Torque Requirements and Tools
| Thread Type | Typical Torque Range | Recommended Tools | Installation Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| M12-M16 | 8-12 Nm | Standard wrench | 45-60 seconds |
| M20-M25 | 15-25 Nm | Torque wrench recommended | 60-90 seconds |
| M32+ | 25-40 Nm | Torque wrench required | 90-120 seconds |
| PG7-PG16 | 6-15 Nm | Standard wrench | 30-45 seconds |
| PG21+ | 15-30 Nm | Torque wrench recommended | 45-75 seconds |
Common Installation Challenges
Hassan’s Dubai facility highlighted several installation considerations we hadn’t initially anticipated:
High-Temperature Installation Issues:
- Metal expansion affects thread engagement
- Seal material becomes more pliable
- Torque values may need adjustment
- Thread compounds may flow differently
Our Recommended Solutions:
- Temperature-compensated torque specifications
- High-temperature thread sealants
- Specialized installation procedures for extreme conditions
- Enhanced training for installation teams
Space Constraints:
- M-type threads require more wrench turns in tight spaces
- PG threads may be preferable for confined installations
- Consider hex vs. knurled grip designs for accessibility
- Panel thickness affects thread engagement length
Installation Quality Control
Critical Checkpoints for Both Systems:
- Thread engagement verification – minimum 5 full threads
- Torque specification compliance – use calibrated tools
- Seal compression check – visual inspection of O-ring deformation
- Final positioning – ensure proper cable entry alignment
- IP rating verification – pressure test when required
Remember, proper installation is more critical than thread type selection for achieving specified performance levels.
What Are the Regional and Industry Preferences?
Understanding market preferences helps predict equipment compatibility and sourcing advantages for your projects.
European markets traditionally favor PG-type threads due to German industrial influence, while North American and Asian markets increasingly adopt M-type threads for global standardization, with specific industries showing strong preferences based on historical equipment choices and regulatory requirements.
Geographic Market Analysis
European Market Preferences:
- Germany: Strong PG-type preference in traditional industries
- UK: Mixed usage with trend toward M-type for new installations
- Scandinavia: Predominantly M-type for offshore and marine applications
- Eastern Europe: Transitioning from PG to M-type for EU standardization
North American Trends:
- United States: Predominantly M-type with some PG in German equipment
- Canada: Similar to US with additional metric standardization push
- Mexico: Following North American trends for NAFTA compatibility
Asian Market Dynamics:
- China: Heavily M-type focused for export compatibility
- Japan: Mixed usage with preference for precision M-type applications
- South Korea: Predominantly M-type for electronics and automotive
- India: M-type preference for new installations, PG legacy systems
Industry-Specific Preferences
Automotive Industry:
- Overwhelming M-type preference for global platform compatibility
- Standardization benefits across international manufacturing
- Supply chain efficiency through common threading
Chemical Processing:
- Mixed usage depending on equipment origin
- Performance-driven selection over traditional preferences
- Seal integrity prioritized regardless of thread type
Marine and Offshore:
- Strong M-type preference for harsh environment performance
- International certification requirements favor ISO standards
- Maintenance standardization across global fleets
David’s manufacturing facility exemplifies the North American trend. Initially equipped with mixed PG and M-type systems from various European suppliers, they’re standardizing on M-type threads for several reasons:
- Simplified inventory management – single thread system
- Improved sourcing flexibility – more supplier options
- Enhanced performance – better sealing in their specific application
- Future-proofing – alignment with industry trends
Regulatory and Standards Impact
International Standards Alignment:
- ISO standards increasingly specify M-type threads
- IEC electrical standards reference metric threading
- ATEX and IECEx certifications commonly use M-type specifications
Regional Regulatory Considerations:
- EU machinery directive compatibility
- North American electrical codes
- Asian export requirements
- Middle Eastern project specifications
At Bepto, we maintain comprehensive inventory of both threading systems, but we’ve observed a 70% shift toward M-type threads in new project specifications over the past five years.
Which System Should You Choose for Specific Applications?
Making the right choice requires balancing technical requirements, compatibility needs, and practical considerations specific to your application.
Choose M-type threads for applications requiring superior sealing performance, international compatibility, and future standardization, while selecting PG-type threads for legacy equipment compatibility, rapid installation requirements, and specific European industrial applications where established infrastructure exists.
Application-Specific Recommendations
High-Performance Sealing Applications:
- Marine and offshore installations → M-type preferred
- Chemical processing environments → M-type for superior seal integrity
- Food and pharmaceutical → M-type for hygienic design requirements
- Outdoor telecommunications → M-type for weather resistance
Speed-Critical Installations:
- Large-scale panel building → PG-type for installation efficiency
- Maintenance and retrofit work → Match existing threading
- Emergency repairs → Use whatever’s immediately available
- High-volume production → Consider installation labor costs
Decision Matrix Framework
| Priority Factor | M-Type Advantage | PG-Type Advantage | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sealing Performance | ✓✓✓ | ✓✓ | M-type for critical applications |
| Installation Speed | ✓ | ✓✓✓ | PG-type for volume installations |
| Global Compatibility | ✓✓✓ | ✓ | M-type for international projects |
| Legacy Equipment | ✓ | ✓✓✓ | Match existing system |
| Future Standardization | ✓✓✓ | ✓ | M-type for new designs |
Real-World Selection Examples
Hassan’s Dubai Chemical Plant Decision:
- Challenge: Mixed European equipment with both thread types
- Solution: Gradual standardization on M-type during maintenance cycles
- Results: 30% reduction in spare parts inventory, improved seal performance
- Timeline: 3-year transition plan with immediate benefits
David’s Ohio Manufacturing Upgrade:
- Challenge: Legacy PG system with sealing issues
- Solution: Complete conversion to M-type during facility expansion
- Results: Eliminated IP rating failures, simplified maintenance procedures
- Investment: Higher upfront cost offset by reduced maintenance
Cost-Benefit Analysis Considerations
Initial Investment Factors:
- Cable gland unit costs (typically similar)
- Installation labor differences
- Tooling and training requirements
- Inventory management complexity
Long-Term Operational Costs:
- Maintenance frequency and complexity
- Seal replacement intervals
- Spare parts availability and cost
- System standardization benefits
Risk Assessment:
- Compatibility with future equipment
- Availability of replacement parts
- Technical support accessibility
- Performance reliability in your environment
Making the Final Decision
For New Installations:
- Assess equipment specifications – what do your panels/enclosures use?
- Evaluate performance requirements – how critical is sealing?
- Consider future expansion – will you add more equipment?
- Review supplier capabilities – who can best support your needs?
- Calculate total cost of ownership – beyond initial purchase price
For Retrofit/Replacement:
- Document existing threading – avoid compatibility issues
- Evaluate performance gaps – is current system adequate?
- Consider partial upgrades – focus on critical applications first
- Plan transition strategy – minimize operational disruption
- Establish new standards – prevent future mixing
Conclusion
The choice between M-type and PG-type threads isn’t just about technical specifications – it’s about aligning your cable management strategy with performance requirements, operational efficiency, and long-term standardization goals. M-type threads offer superior sealing performance and global compatibility, making them ideal for demanding applications and international projects. PG-type threads provide installation speed advantages and compatibility with established European industrial infrastructure. Consider David’s lesson about compatibility planning and Hassan’s successful standardization approach when making your decision. At Bepto, we support both threading systems with comprehensive product lines, certifications, and technical expertise to ensure your choice delivers optimal performance regardless of which path you choose. The key is making an informed decision based on your specific requirements rather than following industry trends blindly.
FAQs About M-Type vs PG-Type Cable Gland Threads
Q: Can I use adapters to convert between M-type and PG-type threads?
A: Yes, thread adapters exist but they add complexity, potential leak points, and increased installation height. Direct threading compatibility is always preferable for reliability and performance. Use adapters only for temporary solutions or when equipment replacement isn’t feasible.
Q: Which thread type is more expensive to purchase and maintain?
A: Initial purchase costs are typically similar, but M-type threads often provide better long-term value through superior sealing performance and reduced maintenance requirements. PG-type threads may offer lower installation labor costs due to faster threading.
Q: How do I identify which thread type my existing equipment uses?
A: Check equipment nameplates, documentation, or measure the thread pitch directly. M-type threads typically have 1.5mm pitch, while PG threads vary by size. When in doubt, consult with your equipment supplier or use thread gauges for accurate identification.
Q: Are there performance differences in harsh environmental conditions?
A: M-type threads generally perform better in extreme conditions due to finer pitch providing more sealing surfaces and better seal compression control. Both systems can achieve high IP ratings, but M-type threads maintain performance more consistently over time.
Q: Should I standardize on one thread type for my entire facility?
A: Standardization offers significant benefits including reduced inventory, simplified maintenance, and improved technician familiarity. Choose M-type for new facilities or when planning major upgrades, but consider transition costs and timing for existing mixed systems.
-
View the official documentation and scope of the ISO 262 standard for general purpose metric screw threads. ↩
-
Learn about the DIN 40430 standard, which defines the specifications for Stahlpanzerrohrgewinde (PG) threads. ↩
-
Explore the history and original application of the “Panzer-Gewinde” or “armor thread” standard in electrical installations. ↩
-
Understand the requirements and challenges of a washdown environment, particularly in the food and beverage industry. ↩
-
Discover how accelerated aging tests are used to predict the long-term performance and lifespan of industrial materials. ↩



