Electromagnetic interference wreaks havoc on sensitive electronic systems, causing equipment failures, data corruption, and costly production downtime that can cost manufacturers millions annually. Many engineers struggle with EMI issues, often discovering shielding problems only after expensive equipment installations are complete, leading to emergency retrofits and extended troubleshooting that disrupts operations and damages reputation. EMC cable glands provide essential electromagnetic interference shielding by creating continuous 360-degree electrical continuity between cable shields and equipment enclosures, featuring conductive materials, specialized sealing elements, and precise engineering that maintains signal integrity while preventing EMI ingress and egress – proper EMC cable gland selection and installation ensures regulatory compliance, protects sensitive electronics, and maintains reliable system performance in electromagnetically challenging environments. After helping countless customers resolve EMI challenges across automotive manufacturing plants, medical device facilities, and telecommunications installations throughout my decade in the cable gland industry, I’ve learned that understanding EMC principles and proper product selection makes the difference between flawless system operation and costly electromagnetic compatibility1 failures.
Table of Contents
- What Are EMC Cable Glands and Why Do They Matter?
- How Do EMC Cable Glands Provide Electromagnetic Shielding?
- What Are the Key Benefits of Using EMC Cable Glands?
- How Do You Select the Right EMC Cable Gland for Your Application?
- What Installation Best Practices Ensure Optimal EMC Performance?
- FAQs About EMC Cable Glands
What Are EMC Cable Glands and Why Do They Matter?
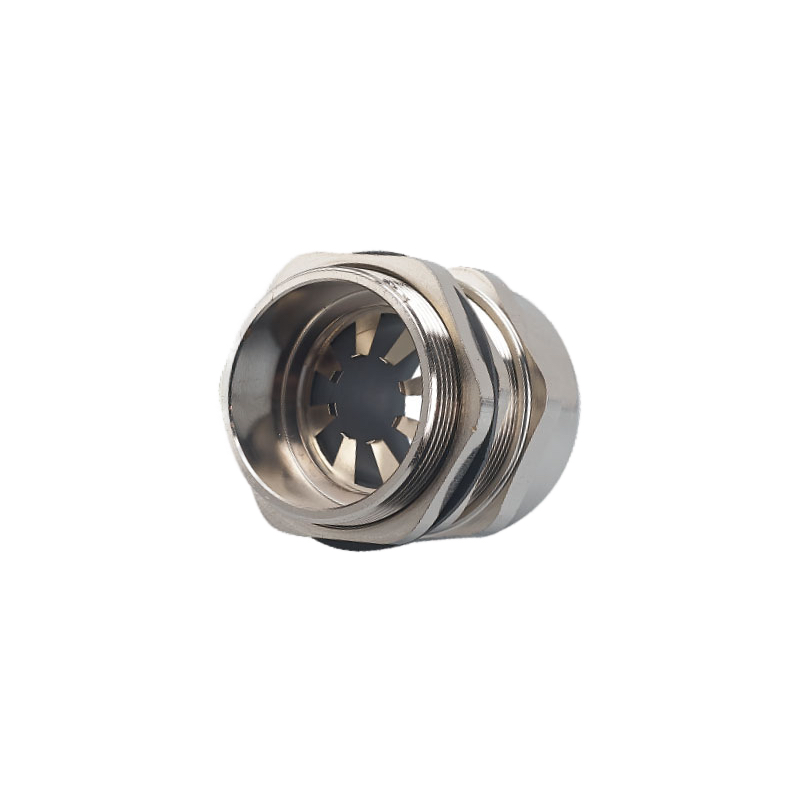
Understanding EMC cable glands is crucial for any engineer dealing with sensitive electronic equipment in today’s electromagnetically noisy environment. EMC cable glands are specialized cable entry devices designed to maintain electromagnetic compatibility by providing continuous electrical shielding between cable armor or braided shields and equipment enclosures, preventing electromagnetic interference from entering or escaping through cable entry points while maintaining environmental sealing – they combine traditional cable gland sealing functions with advanced EMI shielding capabilities essential for regulatory compliance and reliable electronic system operation.
Core EMC Principles
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) encompasses two fundamental aspects: electromagnetic interference (EMI) immunity and electromagnetic emission control. EMC cable glands address both by creating Faraday cage continuity2.
Shielding Effectiveness measures how well EMC cable glands attenuate electromagnetic fields, typically expressed in decibels (dB). Quality EMC cable glands achieve 60-80 dB shielding effectiveness across broad frequency ranges.
360-Degree Continuity ensures complete electrical connection between cable shields and equipment enclosures, eliminating gaps that could allow EMI penetration or emission.
Regulatory Requirements
International Standards including IEC 61000 series3, EN 55022, and FCC Part 15 mandate EMC compliance for electronic equipment, making proper EMC cable gland selection essential for regulatory approval.
Industry-Specific Requirements vary significantly – medical devices require IEC 60601-1-2 compliance, automotive systems follow ISO 11452 standards, while industrial equipment must meet EN 61000-6-2 immunity requirements.
Certification Testing validates EMC cable gland performance through standardized test procedures measuring shielding effectiveness, transfer impedance4, and coupling attenuation across specified frequency ranges.
Marcus, the chief electrical engineer at BMW’s Leipzig manufacturing facility in Germany, contacted us after experiencing intermittent robot control failures during production. Their standard cable glands allowed EMI from welding equipment to interfere with sensitive servo motor controllers, causing costly line stoppages. We provided our brass EMC cable glands with integrated EMI gaskets, achieving 70 dB shielding effectiveness. The installation eliminated interference issues, improved production reliability by 99.2%, and ensured compliance with automotive EMC standards while maintaining the robust environmental sealing required for their harsh manufacturing environment.
How Do EMC Cable Glands Provide Electromagnetic Shielding?
The electromagnetic shielding mechanism of EMC cable glands relies on sophisticated engineering principles that create effective barriers against electromagnetic interference. EMC cable glands provide electromagnetic shielding through conductive housing materials, specialized EMI gaskets, cable shield termination systems, and precise mechanical design that creates continuous electrical paths between cable shields and equipment enclosures – the combination of reflection, absorption, and multiple shielding barriers attenuates electromagnetic fields across wide frequency ranges while maintaining environmental sealing and mechanical integrity essential for industrial applications.
Shielding Mechanisms
Reflection Shielding occurs when electromagnetic waves encounter conductive surfaces, with most energy reflected back rather than penetrating the barrier. EMC cable glands utilize brass, stainless steel, or nickel-plated materials for optimal reflection characteristics.
Absorption Shielding converts electromagnetic energy to heat through conductive and magnetic materials. Specialized EMI gaskets containing conductive particles enhance absorption while maintaining flexibility for reliable sealing.
Multiple Barrier Design employs layered shielding approaches with primary housing shielding, secondary gasket barriers, and cable shield termination creating redundant protection against EMI penetration.
Construction Elements
Conductive Housing Materials include brass alloys, stainless steel, and specialized zinc alloys with nickel plating providing corrosion resistance while maintaining excellent electrical conductivity for effective shielding.
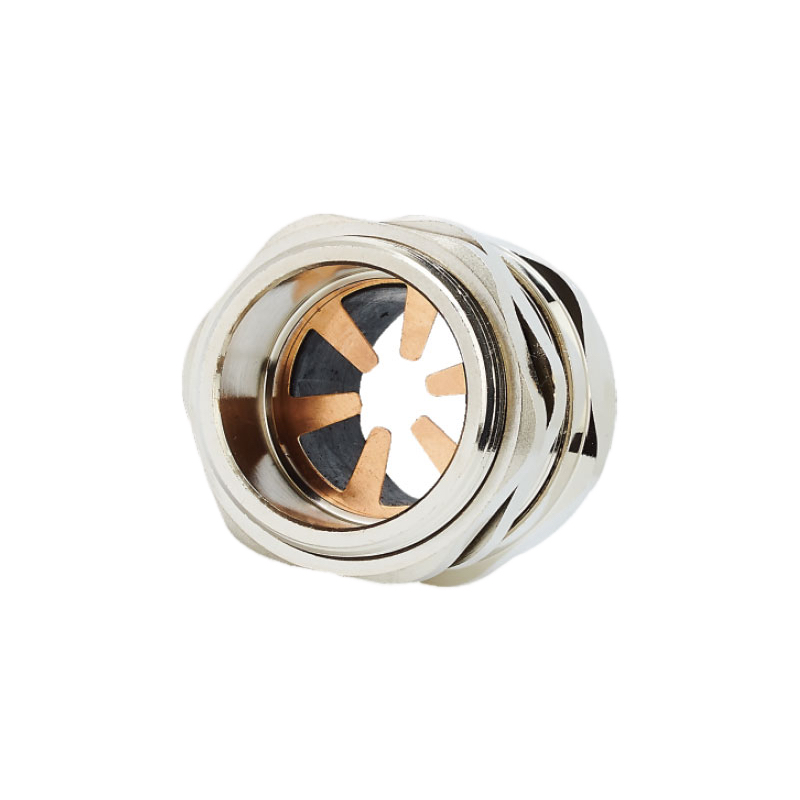
EMI Gaskets and Seals feature conductive elastomers, metal-filled polymers, or knitted wire mesh elements that maintain electrical continuity while providing environmental sealing against moisture, dust, and chemical ingress.
Cable Shield Termination systems ensure proper electrical connection between cable armor, braided shields, or foil shields and the EMC cable gland housing through compression fittings, clamping mechanisms, or conductive adhesives.
Performance Characteristics
Frequency Response varies with EMC cable gland design, with quality products providing effective shielding from 10 kHz to 18 GHz covering most industrial EMI sources and sensitive equipment operating frequencies.
Transfer Impedance measurements quantify shielding effectiveness, with premium EMC cable glands achieving transfer impedance values below 1 milliohm across critical frequency ranges.
Environmental Durability ensures long-term shielding performance despite temperature cycling, vibration, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress through robust material selection and precision manufacturing.
What Are the Key Benefits of Using EMC Cable Glands?
EMC cable glands deliver significant advantages that justify their investment through improved system reliability, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency. Key benefits of EMC cable glands include superior electromagnetic interference protection that prevents equipment malfunctions and data corruption, regulatory compliance assurance for international market access, enhanced system reliability through reduced EMI-related failures, cost savings from eliminated troubleshooting and retrofits, and future-proofing against increasingly stringent EMC requirements – these advantages make EMC cable glands essential investments for any application involving sensitive electronic equipment in electromagnetically challenging environments.

Operational Advantages
Equipment Protection prevents EMI-induced failures, data corruption, and performance degradation in sensitive electronic systems, eliminating costly downtime and repair expenses.
System Reliability improves dramatically with proper EMC cable gland implementation, reducing unplanned maintenance, extending equipment life, and ensuring consistent operational performance.
Troubleshooting Elimination removes EMI-related intermittent faults that consume engineering time and resources while creating customer satisfaction issues and warranty claims.
Compliance Benefits
Regulatory Approval becomes straightforward with proper EMC cable gland selection, ensuring products meet international EMC standards without expensive redesign or retrofitting.
Market Access expands globally as EMC compliance enables product sales in regulated markets including Europe, North America, and Asia-Pacific regions with strict EMC requirements.
Certification Confidence provides assurance during EMC testing phases, reducing risk of test failures and associated delays in product launches or facility approvals.
Economic Value
Initial Cost Justification through prevention of expensive EMI remediation, equipment replacement, and production delays that far exceed EMC cable gland investment costs.
Long-term Savings accumulate through reduced maintenance, extended equipment life, improved productivity, and elimination of EMI-related quality issues affecting customer satisfaction.
Risk Mitigation protects against regulatory fines, product recalls, customer complaints, and reputation damage associated with EMC non-compliance or EMI-related failures.
Dr. Sarah Chen, R&D director at Siemens Medical Solutions in Erlangen, Germany, faced critical EMI challenges during MRI system development. Standard cable glands allowed electromagnetic interference that affected image quality and patient safety systems. Our stainless steel EMC cable glands with specialized medical-grade EMI gaskets achieved 80 dB shielding effectiveness, ensuring IEC 60601-1-2 compliance. The solution eliminated interference issues, accelerated regulatory approval by six months, and enabled successful product launch in global markets while maintaining the stringent reliability standards required for life-critical medical equipment applications.
How Do You Select the Right EMC Cable Gland for Your Application?
Proper EMC cable gland selection requires careful evaluation of multiple technical factors to ensure optimal electromagnetic shielding performance and long-term reliability. Select the right EMC cable gland by evaluating shielding effectiveness requirements based on EMI sources and sensitive equipment frequencies, choosing appropriate housing materials for environmental conditions, matching cable shield types and termination methods, considering installation constraints and maintenance access, and ensuring compliance with relevant EMC standards – systematic selection methodology prevents costly mistakes while optimizing performance, reliability, and total cost of ownership for specific application requirements.
Technical Requirements Assessment
EMI Environment Analysis identifies electromagnetic interference sources, frequency ranges, field strengths, and sensitive equipment susceptibility levels to determine required shielding effectiveness specifications.
Cable Shield Compatibility ensures EMC cable glands properly terminate braided shields, foil shields, armored cables, or combination shielding systems with appropriate compression and electrical contact methods.
Environmental Conditions including temperature ranges, chemical exposure, moisture levels, vibration, and mechanical stress influence material selection and sealing system requirements for long-term performance.
Material Selection Criteria
| Application Type | Recommended Material | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Marine/Offshore | Stainless Steel 316L | Superior corrosion resistance |
| Chemical Processing | Stainless Steel 316L | Chemical compatibility |
| General Industrial | Nickel-Plated Brass | Cost-effective performance |
| Food/Pharmaceutical | Stainless Steel 316L | Hygiene compliance |
| Telecommunications | Brass with EMI Gaskets | Electrical performance |
Performance Specifications
Shielding Effectiveness requirements typically range from 40 dB for basic applications to 100+ dB for critical military or medical applications, with most industrial applications requiring 60-80 dB performance.
Frequency Range considerations must cover both EMI sources and sensitive equipment operating frequencies, with broadband performance from 10 kHz to 18 GHz preferred for comprehensive protection.
Transfer Impedance specifications below 1 milliohm ensure effective shielding across critical frequency ranges while maintaining low resistance paths for proper grounding and EMI mitigation.
Installation Considerations
Thread Compatibility with equipment enclosures including metric, NPT, and PG threading systems5 ensures proper mechanical and electrical connection without adaptation requirements.
Cable Entry Size ranges must accommodate cable diameters with appropriate sealing compression while maintaining EMI gasket contact pressure for effective shielding performance.
Maintenance Access requirements influence EMC cable gland design selection, with some applications requiring field-serviceable EMI gaskets while others prioritize permanent installation reliability.
What Installation Best Practices Ensure Optimal EMC Performance?
Proper installation techniques are critical for achieving specified EMC cable gland shielding effectiveness and long-term reliability. Installation best practices for optimal EMC performance include ensuring clean, conductive mounting surfaces free from paint or coatings, proper torque application to maintain EMI gasket compression and electrical contact, correct cable shield preparation and termination, verification of electrical continuity between cable shields and equipment enclosures, and regular inspection of EMI gasket condition – following systematic installation procedures prevents shielding degradation while ensuring reliable electromagnetic compatibility throughout the system service life.
Surface Preparation
Mounting Surface Cleaning removes paint, coatings, oxidation, and contaminants that could interfere with electrical contact between EMC cable glands and equipment enclosures, ensuring optimal shielding effectiveness.
Conductivity Verification confirms proper electrical connection through continuity testing between EMC cable gland housing and equipment enclosure, identifying potential contact issues before final installation.
Thread Preparation includes proper thread cutting, deburring, and cleaning to ensure secure mechanical connection and optimal electrical contact without damage to EMI sealing elements.
Cable Preparation Techniques
Shield Termination requires careful cable preparation with proper shield length, conductor separation, and termination hardware to ensure reliable electrical connection without shield damage or contamination.
Strain Relief prevents mechanical stress on cable shields and EMC cable gland connections through proper cable routing, support, and strain relief hardware that maintains shield integrity.
Environmental Sealing verification ensures primary and secondary sealing elements provide required IP ratings while maintaining EMI gasket compression for effective electromagnetic shielding.
Quality Verification
Continuity Testing confirms electrical connection between cable shields and equipment ground through low-resistance measurements, typically requiring less than 10 milliohms total resistance.
Shielding Effectiveness Testing may be required for critical applications using specialized EMI test equipment to verify actual shielding performance meets specification requirements.
Documentation Requirements include installation records, test results, and maintenance schedules ensuring traceability and compliance with quality management systems and regulatory requirements.
Maintenance Procedures
Periodic Inspection schedules should include EMI gasket condition assessment, electrical continuity verification, and environmental seal integrity checking to maintain long-term EMC performance.
Gasket Replacement procedures ensure proper EMI gasket selection, installation torque, and performance verification when maintenance or equipment modifications require EMC cable gland servicing.
Performance Monitoring through system EMC testing or EMI monitoring can identify degraded shielding effectiveness requiring EMC cable gland maintenance or replacement for continued compliance.
Conclusion
EMC cable glands represent essential components for maintaining electromagnetic compatibility in today’s electronically complex industrial environment. Proper selection based on shielding effectiveness requirements, environmental conditions, and cable shield compatibility ensures optimal EMI protection while meeting regulatory compliance standards. Installation best practices including surface preparation, proper torque application, and shield termination techniques maximize long-term performance and reliability. At Bepto, we’re committed to providing comprehensive EMC cable gland solutions with expert technical support, proven quality certifications, and cost-effective performance that protects your sensitive equipment investments while ensuring regulatory compliance! 😉
FAQs About EMC Cable Glands
Q: What’s the difference between EMC cable glands and regular cable glands?
A: EMC cable glands provide electromagnetic interference shielding through conductive materials and EMI gaskets while regular cable glands only offer environmental sealing. EMC versions maintain electrical continuity between cable shields and equipment enclosures for EMI protection.
Q: How do I know what shielding effectiveness I need?
A: Shielding effectiveness requirements depend on EMI sources and sensitive equipment susceptibility levels. Most industrial applications require 60-80 dB effectiveness, while critical medical or military applications may need 100+ dB performance.
Q: Can EMC cable glands work with different cable shield types?
A: Yes, quality EMC cable glands accommodate braided shields, foil shields, armored cables, and combination shielding systems through appropriate termination hardware and compression mechanisms designed for each shield type.
Q: What maintenance do EMC cable glands require?
A: EMC cable glands need periodic inspection of EMI gasket condition, electrical continuity testing, and environmental seal verification. EMI gaskets may require replacement every 5-10 years depending on environmental conditions and application requirements.
Q: Are there different EMC cable gland materials for different applications?
A: Yes, stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance for harsh environments, brass provides cost-effective performance for general industrial use, while specialized materials like nickel-plated options enhance conductivity and environmental resistance for specific applications.
-
Get a clear definition of Electromagnetic Compatibility and its core principles. ↩
-
Learn the physics of how a Faraday cage provides electrical continuity and shielding. ↩
-
See an overview of the IEC 61000 international standards for EMC. ↩
-
Understand the technical definition of transfer impedance and how it measures shielding effectiveness. ↩
-
See a comparison guide for NPT, PG, and metric threading standards. ↩