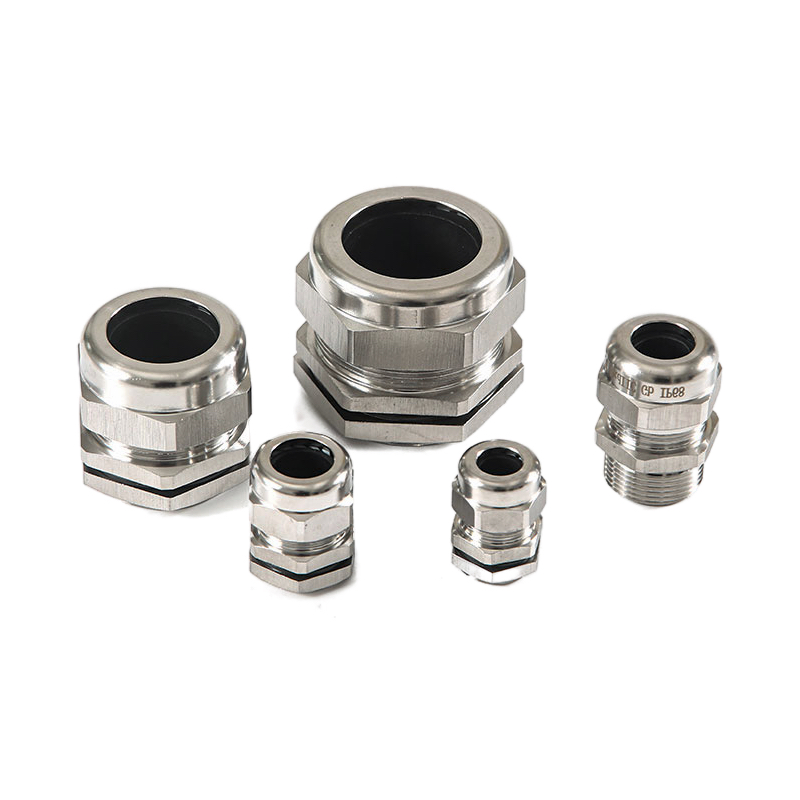
Choosing the wrong cable gland for your NEMA-rated enclosure can lead to costly equipment failures and safety hazards.
NEMA enclosure ratings define specific protection levels against environmental factors, and your cable gland must match or exceed these requirements to maintain the enclosure’s integrity and ensure optimal performance.
Last week, I helped David, a procurement manager from a major automation company, avoid a $50,000 mistake by selecting the correct IP-rated cable glands for his NEMA 4X enclosures.
Table of Contents
- What Are NEMA Enclosure Ratings and Why Do They Matter?
- How Do NEMA Ratings Compare to IP Ratings for Cable Glands?
- Which Cable Gland Materials Work Best with Different NEMA Ratings?
- What Common Mistakes Should You Avoid When Selecting Cable Glands?
What Are NEMA Enclosure Ratings and Why Do They Matter?
Understanding NEMA ratings is crucial for protecting your electrical equipment from environmental hazards.
NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association)1 ratings classify enclosures based on their ability to protect against dust, water, corrosion, and other environmental factors, with ratings ranging from NEMA 1 (basic indoor protection) to NEMA 6P (submersion protection).
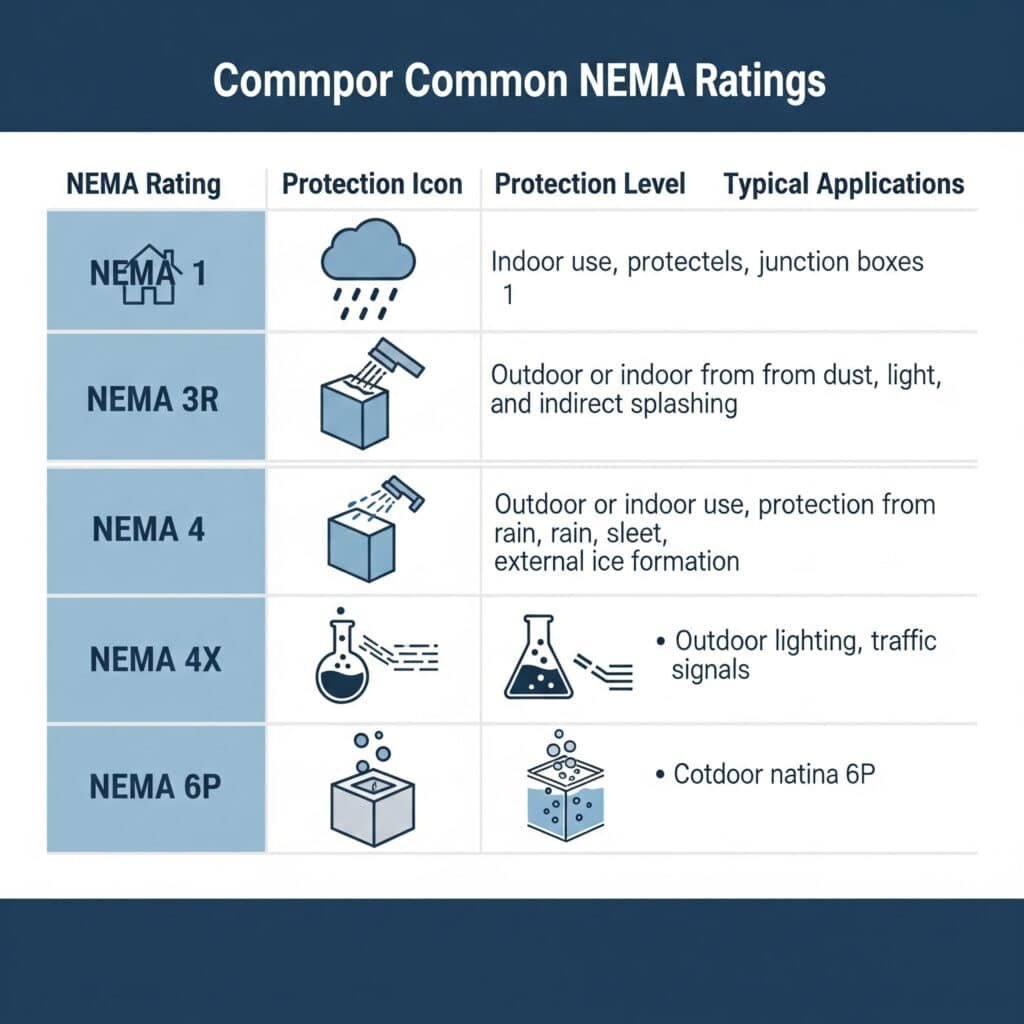
Common NEMA Ratings and Their Applications
| NEMA Rating | Protection Level | Typical Applications | Required Cable Gland Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| NEMA 1 | Indoor, basic | Control panels, switchgear | Basic sealing, standard materials |
| NEMA 3R | Outdoor, rain-resistant | Outdoor electrical boxes | Weather-resistant sealing |
| NEMA 4 | Watertight | Food processing, washdown areas | IP65/IP66 equivalent sealing |
| NEMA 4X | Corrosion-resistant | Chemical plants, marine environments | Stainless steel or special coatings |
| NEMA 6P | Submersible | Underground installations | IP68 rating, enhanced sealing |
Why Cable Gland Selection Matters
The cable entry point is often the weakest link in any enclosure system. I’ve seen countless cases where engineers spec’d the perfect NEMA-rated enclosure but compromised the entire system with inadequate cable glands.
Key considerations include:
- Sealing integrity: Your cable gland must maintain the enclosure’s IP rating
- Material compatibility: Corrosive environments require specific materials
- Temperature range: Ensure gaskets and seals can handle operating conditions
How Do NEMA Ratings Compare to IP Ratings for Cable Glands?
Most cable glands use IP ratings, which can be confusing when working with NEMA-rated enclosures.
NEMA and IP ratings2 serve similar purposes but use different testing standards – NEMA 4 roughly equals IP65/IP66, while NEMA 6P corresponds to IP68, though direct conversions aren’t always exact.
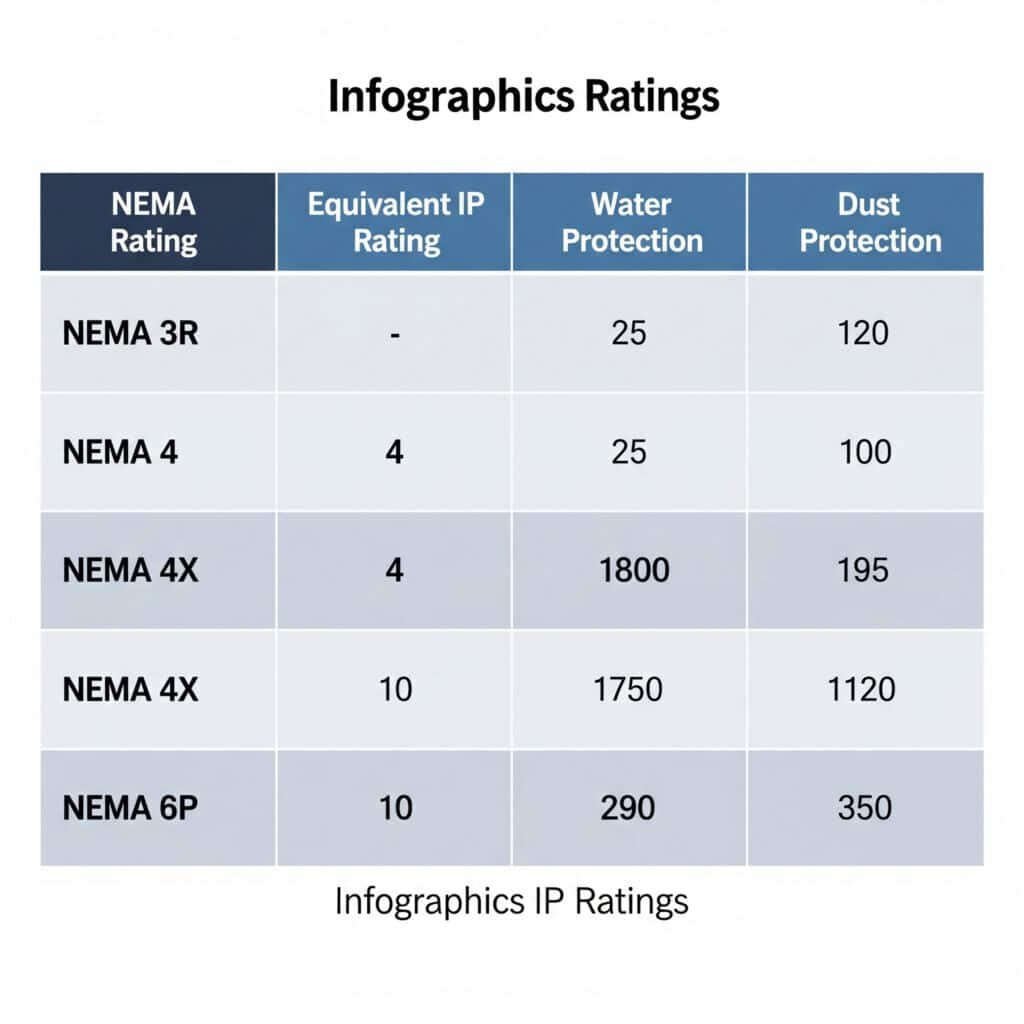
NEMA to IP Conversion Guide
Here’s the practical conversion chart I use with my customers:
| NEMA Rating | Equivalent IP Rating | Water Protection | Dust Protection |
|---|---|---|---|
| NEMA 3R | IP24 | Rain-resistant | Limited dust protection |
| NEMA 4 | IP65/IP66 | Water jets | Dust-tight |
| NEMA 4X | IP65/IP66 | Water jets + corrosion resistance | Dust-tight |
| NEMA 6P | IP68 | Continuous submersion | Dust-tight |
Real-World Application Example
Hassan, who runs a petrochemical facility, needed cable glands for NEMA 4X enclosures in a highly corrosive environment. We provided stainless steel cable glands with IP66 rating and ATEX certification3. The key was ensuring the cable gland’s corrosion resistance matched the enclosure’s 4X rating while maintaining proper sealing performance.
Which Cable Gland Materials Work Best with Different NEMA Ratings?
Material selection directly impacts your cable gland’s ability to maintain NEMA protection levels.
For NEMA 1-3R applications, nylon cable glands offer cost-effective protection, while NEMA 4X and marine environments require stainless steel or brass with specialized coatings to prevent corrosion and maintain long-term sealing integrity.
Material Selection Matrix
Nylon Cable Glands:
- Best for: NEMA 1, 3R applications
- Advantages: Cost-effective, chemical resistant, lightweight
- Limitations: UV degradation, temperature limitations
- Our recommendation: PA66 nylon with UV stabilizers
Brass Cable Glands:
- Best for: NEMA 4 indoor applications
- Advantages: Excellent conductivity, EMC shielding4
- Limitations: Corrosion in marine environments
- Our recommendation: Nickel-plated brass for enhanced protection
Stainless Steel Cable Glands:
- Best for: NEMA 4X, 6P, marine applications
- Advantages: Superior corrosion resistance, high temperature tolerance
- Applications: Chemical plants, offshore platforms, food processing
- Our recommendation: 316L stainless steel for maximum corrosion resistance
Gasket and Seal Considerations
The gasket material is equally critical:
- NBR (Nitrile): Standard applications, good oil resistance
- EPDM: Excellent weather resistance for outdoor NEMA 3R/4 applications
- Viton: High-temperature and chemical resistance for demanding NEMA 4X environments
What Common Mistakes Should You Avoid When Selecting Cable Glands?
Even experienced engineers make critical errors that compromise enclosure protection.
The most common mistakes include mismatching IP ratings with NEMA requirements, ignoring cable outer diameter tolerances, and overlooking long-term material compatibility in corrosive environments.
Top 5 Selection Mistakes
1. Assuming All IP65 Glands Work with NEMA 4
Not all IP65 cable glands meet NEMA 4 testing requirements. Always verify the manufacturer has conducted proper NEMA testing, not just IP testing.
2. Ignoring Cable Diameter Ranges
I’ve seen projects delayed because the specified cable gland couldn’t accommodate the actual cable diameter. Always check:
- Minimum and maximum cable diameters
- Jacket material compatibility
- Strain relief requirements
3. Overlooking Thread Compatibility
Mixing metric and NPT threads5 is a recipe for disaster. Ensure your cable gland threads match the enclosure’s threaded entries perfectly.
4. Inadequate Corrosion Protection
David’s company initially wanted to use standard brass glands in a coastal environment. We switched to stainless steel, preventing potential failures and warranty claims.
5. Forgetting About Maintenance Access
Choose cable glands that allow for easy cable replacement without compromising the seal. Our quick-disconnect designs have saved customers significant maintenance time.
Quality Verification Checklist
Before finalizing your selection:
- ✅ Verify NEMA test certificates (not just IP ratings)
- ✅ Confirm material compatibility with your environment
- ✅ Check cable diameter compatibility
- ✅ Ensure proper thread specifications
- ✅ Validate temperature and pressure ratings
Conclusion
Proper cable gland selection ensures your NEMA-rated enclosures maintain their protective integrity throughout their service life.
FAQs About NEMA Cable Gland Selection
Q: Can I use IP65 cable glands with NEMA 4 enclosures?
A: Generally yes, but verify the manufacturer has conducted NEMA testing. IP65 and NEMA 4 have similar protection levels, but testing standards differ. We always recommend cable glands specifically tested and certified for NEMA compliance.
Q: What’s the difference between NEMA 4 and NEMA 4X cable gland requirements?
A: NEMA 4X adds corrosion resistance to NEMA 4’s water protection. This typically requires stainless steel construction or special anti-corrosion coatings. Standard brass or nylon glands suitable for NEMA 4 may not meet 4X corrosion requirements.
Q: How do I determine the correct cable gland size for my application?
A: Measure your cable’s outer diameter and select a gland with a sealing range that encompasses this dimension. Allow for tolerance variations and consider future cable changes. Our technical team can help verify compatibility.
Q: Are there special requirements for NEMA 6P submersible applications?
A: Yes, NEMA 6P requires IP68 rating with continuous submersion capability. Use cable glands with enhanced sealing systems, typically featuring double O-ring designs and pressure-tested seals. Material selection becomes critical for long-term underwater exposure.
Q: Can I retrofit existing enclosures with higher-rated cable glands?
A: Often yes, but the enclosure’s overall rating is limited by its weakest component. Upgrading cable glands alone won’t increase the enclosure’s NEMA rating unless all components meet the higher standard. Consult the enclosure manufacturer for guidance.
-
Visit the official website of NEMA to learn more about their standards and mission. ↩
-
Understand the International Electrotechnical Commission’s standard for Ingress Protection (IP) ratings. ↩
-
Learn about the European Union’s directives for equipment used in potentially explosive environments. ↩
-
Discover the principles of EMC and how shielding protects electronic devices from interference. ↩
-
Compare the specifications and use cases for NPT and other common thread standards. ↩



