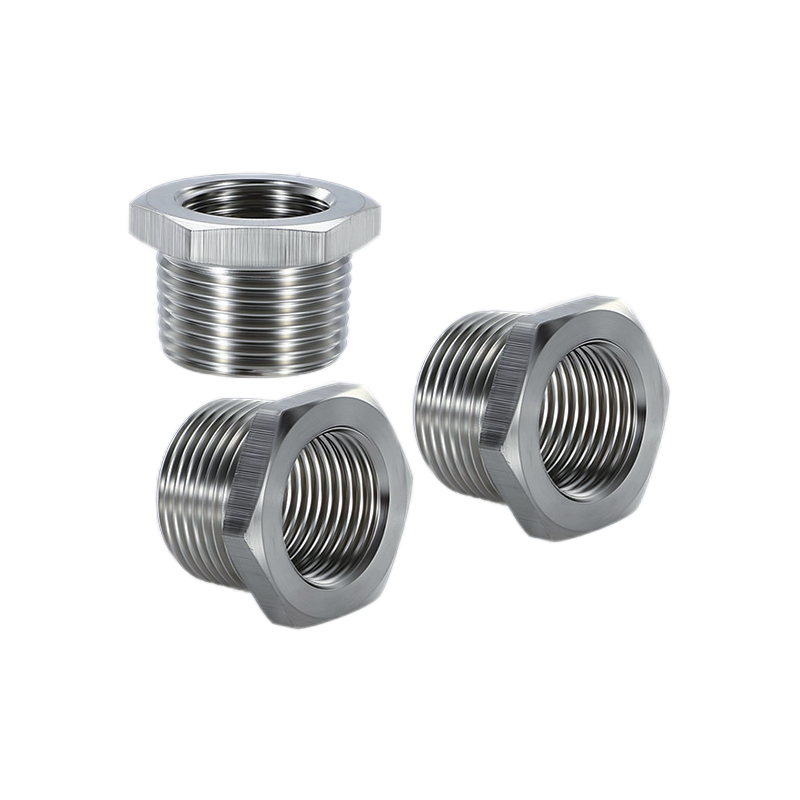
Wrong thread selection can destroy your equipment and create dangerous installation failures. Thread mismatches cause leaks, poor connections, and costly project delays.
Cable gland thread conversion requires understanding NPT (tapered), PG (German standard), and metric threading systems. Use proper adapters, verify pitch specifications, and ensure IP rating compatibility for safe installations.
Last week, David called me frantically from his production floor. His team had ordered 500 cable glands with PG threads, but their panels were metric. The delivery deadline was just 48 hours away.
Table of Contents
- What Are the Key Differences Between NPT, PG, and Metric Threads?
- How Do You Calculate Thread Conversion Requirements Accurately?
- Which Thread Adapters Provide the Most Reliable Conversion?
- What Are the Common Pitfalls in Thread Conversion Projects?
What Are the Key Differences Between NPT, PG, and Metric Threads?
Understanding these threading systems prevents costly mistakes and ensures proper sealing performance.
NPT threads are tapered for pipe connections, PG threads use German DIN standards with straight profiles, and metric threads follow ISO standards. Each system has unique pitch, angle, and sealing characteristics.
Thread System Comparison
| Thread Type | Origin | Profile | Sealing Method | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NPT | USA | Tapered (1:16) | Thread interference | North American panels |
| PG | Germany | Straight | O-ring/gasket | European equipment |
| Metric (M) | International | Straight | O-ring/gasket | Global standard |
NPT (National Pipe Thread) Characteristics
NPT threads create sealing through interference fit1:
- Taper rate: 1:16 (3.175mm per 25.4mm)
- Thread angle: 60 degrees
- Pitch: Varies by size (14 TPI2 for 1/2″, 11.5 TPI for 3/4″)
- Sealing: No gasket required when properly installed
PG (Panzer-Gewinde) Specifications
German PG standard features:
- Profile: Straight threads
- Thread angle: 55 degrees
- Pitch: Coarse (typically 1.5-2.0mm)
- Sealing: Requires O-ring or gasket
- Sizes: PG7, PG9, PG11, PG13.5, PG16, PG21, PG29, PG36, PG42, PG48
Metric Thread Details
ISO metric threads offer:
- Profile: Straight threads
- Thread angle: 60 degrees
- Pitch: Fine (0.5-2.0mm depending on diameter)
- Sealing: O-ring or gasket required
- Sizes: M12, M16, M20, M25, M32, M40, M50, M63
When Hassan’s refinery needed to retrofit American equipment with European cable glands, we provided a complete conversion chart and recommended adapters. The project saved them 40% compared to replacing entire panels.
Regional Preferences
Different regions favor specific threading:
- North America: Primarily NPT
- Europe: PG and Metric
- Asia: Metric dominant
- Middle East: Mixed (depends on equipment origin)
How Do You Calculate Thread Conversion Requirements Accurately?
Precise calculations prevent installation failures and ensure proper sealing performance.
Thread conversion requires matching outer diameter, thread pitch3, and sealing requirements. Use conversion charts, verify with thread gauges, and account for adapter thickness when calculating panel cutout requirements.
Essential Conversion Formulas
NPT to Metric Conversion
For NPT to metric conversion, consider:
- Major diameter: NPT nominal size ≠ actual diameter
- Thread engagement: Minimum 4-5 full threads
- Sealing compound: Required for NPT connections
Common Size Equivalents
| NPT Size | Actual OD (mm) | Metric Equivalent | PG Equivalent |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1/2″ | 21.34 | M20 x 1.5 | PG16 |
| 3/4″ | 26.67 | M25 x 1.5 | PG21 |
| 1″ | 33.40 | M32 x 1.5 | PG29 |
| 1-1/4″ | 42.16 | M40 x 1.5 | PG36 |
| 1-1/2″ | 48.26 | M50 x 1.5 | PG42 |
Measurement Verification Methods
Thread Pitch Gauges
Always verify thread pitch using:
- Metric pitch gauge: For metric threads
- TPI gauge: For NPT threads
- PG gauge: For German PG threads
Critical Measurements
Before ordering adapters, measure:
- Thread diameter: Use calipers for accuracy
- Thread pitch: Use appropriate gauge
- Panel thickness: Affects adapter selection
- Available space: For adapter clearance
David’s emergency situation taught us the importance of verification. We now provide measurement kits with our conversion adapters to prevent field surprises.
Calculation Tools and Resources
We’ve developed calculation aids:
- Thread conversion charts: Quick reference guides
- Online calculators: Automated conversion tools
- Mobile apps: Field-friendly calculation tools
- Technical support: Direct engineer consultation
Special Considerations
Temperature Effects
Thread expansion affects conversion:
- Steel adapters: Minimal expansion
- Brass adapters: Moderate expansion
- Aluminum adapters: Higher expansion rates
Pressure Ratings
Conversion may affect pressure ratings:
- NPT connections: Rely on thread interference
- Metric/PG: Depend on O-ring compression
- Adapter materials: Must match application requirements
Which Thread Adapters Provide the Most Reliable Conversion?
Adapter selection determines conversion success and long-term reliability.
High-quality brass or stainless steel adapters with proper O-ring grooves provide reliable thread conversion. Choose adapters with certification matching your application requirements and verify IP rating maintenance.
Adapter Material Selection
Brass Adapters (CuZn39Pb3)
Our most popular choice offers:
- Excellent machinability: Precise thread cutting
- Good corrosion resistance: Suitable for most environments
- Cost-effective: Balance of performance and price
- Easy installation: Standard tools required
Stainless Steel Adapters (316L)
For demanding applications:
- Superior corrosion resistance: Marine and chemical environments
- High strength: Heavy-duty applications
- Temperature resistance: Wide operating range
- Long service life: Minimal maintenance required
Specialized Materials
For extreme conditions:
- Inconel adapters: High-temperature applications
- Hastelloy adapters: Highly corrosive environments
- Titanium adapters: Aerospace and medical applications
Adapter Design Features
Sealing System Design
Reliable adapters incorporate:
- Multiple O-ring grooves: Primary and backup sealing
- Proper groove dimensions: Ensures O-ring compression
- Surface finish: Ra 0.8μm or better for sealing surfaces
- Thread quality: Class 2A/2B minimum
Installation Features
User-friendly design includes:
- Hex flats: For wrench engagement
- Knurled surfaces: Hand-tightening capability
- Length optimization: Minimal panel thickness increase
- Clear marking: Thread identification
Bepto Adapter Advantages
Our adapters feature:
- Precision manufacturing: CNC machined to ±0.05mm
- Quality materials: Certified raw materials only
- Rigorous testing: 100% pressure tested
- Complete documentation: Certificates and test reports
Hassan’s chemical plant project required NPT to metric conversion for 200+ connections. Our stainless steel adapters with Viton O-rings have performed flawlessly for three years in their corrosive environment.
Adapter Selection Criteria
Application Requirements
Consider these factors:
- Environmental conditions: Temperature, chemicals, moisture
- Pressure requirements: System operating pressure
- Vibration levels: Equipment movement and shock
- Maintenance access: Serviceability requirements
Quality Indicators
Look for these features:
- Material certifications: Mill test certificates
- Dimensional accuracy: Precision manufacturing
- Surface finish: Proper sealing surfaces
- Testing documentation: Pressure and leak testing
Installation Best Practices
Proper Installation Sequence
- Clean threads: Remove debris and old sealant
- Apply thread sealant: For NPT connections only
- Hand start: Prevent cross-threading4
- Torque to specification: Use calibrated tools
- Verify sealing: Pressure test installation
Common Installation Errors
Avoid these mistakes:
- Over-tightening: Damages threads and seals
- Wrong sealant: Incompatible materials
- Dirty threads: Causes leaks and damage
- Misaligned installation: Creates stress concentrations
What Are the Common Pitfalls in Thread Conversion Projects?
Avoiding these pitfalls saves time, money, and prevents safety hazards.
Common thread conversion mistakes include mismatched thread pitch, inadequate sealing verification, ignoring temperature effects, and using incompatible materials. Always verify measurements and test installations before final assembly.
Measurement and Specification Errors
Thread Identification Mistakes
The most common errors include:
- Assuming thread type: Visual identification is unreliable
- Confusing similar sizes: PG16 vs M20 confusion
- Ignoring thread pitch: Multiple pitches exist for same diameter
- Misreading specifications: Drawing interpretation errors
Verification Failures
Critical verification steps often skipped:
- Thread gauge testing: Assumption vs. measurement
- Fit testing: Dry assembly before final installation
- Clearance checking: Adapter space requirements
- Panel thickness measurement: Affects thread engagement
Material Compatibility Issues
Galvanic Corrosion
Mixing dissimilar metals causes:
- Accelerated corrosion: Electrochemical reactions
- Joint failure: Weakened connections
- Maintenance problems: Seized connections
Temperature Mismatch
Different expansion rates create:
- Loose connections: Thermal cycling effects
- Seal failure: O-ring compression loss
- Stress concentrations: Cracking potential
David learned this lesson when his aluminum panels with brass adapters loosened after temperature cycling. We redesigned using matched thermal expansion coefficients5.
Installation and Assembly Problems
Torque Specifications
Common torque mistakes:
- Over-tightening: Thread damage and seal extrusion
- Under-tightening: Inadequate sealing
- Wrong tools: Improper torque application
- No verification: Skipping torque checks
Sealing Compound Errors
Sealant application problems:
- Wrong product: Incompatible with system fluids
- Excessive application: Contamination and blockage
- Insufficient coverage: Incomplete sealing
- Mixing products: Chemical incompatibility
Quality Control Failures
Inadequate Testing
Skipped verification steps:
- Pressure testing: Leak detection
- Vibration testing: Connection integrity
- Temperature cycling: Thermal stress testing
- Long-term monitoring: Performance verification
Documentation Gaps
Missing critical information:
- Installation records: Torque values and procedures
- Material certificates: Traceability documentation
- Test results: Performance verification data
- Maintenance schedules: Service requirements
Prevention Strategies
Pre-Project Planning
Successful projects include:
- Detailed specifications: Clear requirements definition
- Material selection: Compatibility verification
- Supplier qualification: Quality system evaluation
- Prototype testing: Proof of concept validation
Quality Assurance Program
Implement these controls:
- Incoming inspection: Material and dimensional verification
- Installation procedures: Standardized methods
- Testing protocols: Systematic verification
- Documentation requirements: Complete record keeping
Hassan’s team now uses our comprehensive conversion checklist for all projects. Their installation success rate improved from 85% to 99.5% after implementing proper verification procedures. 😉
Conclusion
Successful thread conversion requires understanding system differences, precise calculations, quality adapters, and proper installation procedures to ensure reliable performance.
FAQs About Cable Gland Thread Conversion
Q: Can I use NPT cable glands directly in metric threaded panels?
A: No, NPT threads are tapered while metric threads are straight. You need proper thread adapters to ensure sealing and prevent damage to panels or glands.
Q: What’s the difference between PG and metric thread pitch?
A: PG threads typically use coarser pitch (1.5-2.0mm) compared to metric fine pitch (0.5-1.5mm). Always verify with thread gauges before ordering adapters.
Q: How do I maintain IP rating when using thread adapters?
A: Use adapters with proper O-ring grooves, verify seal compression, and ensure adapter material compatibility. Quality adapters maintain original IP ratings when properly installed.
Q: What torque values should I use for thread adapters?
A: Torque depends on thread size and material. Typical values: M20 = 25-30 Nm, M25 = 35-40 Nm. Always follow manufacturer specifications and use calibrated tools.
Q: Can thread adapters handle the same pressure as direct connections?
A: Quality adapters match or exceed direct connection pressure ratings when properly installed. Verify adapter specifications match your system requirements before use.
-
Learn the mechanical engineering principle of an interference fit and how it is used to create strong joints. ↩
-
Understand what TPI (Threads Per Inch) means and how it is measured on imperial and NPT threads. ↩
-
See a guide on how to properly measure thread pitch for both metric (mm) and imperial (TPI) systems. ↩
-
Get practical tips and best practices for preventing cross-threading when installing threaded fasteners. ↩
-
Review a materials engineering table of thermal expansion coefficients for common metals and alloys. ↩