The sound of an explosion in an industrial facility is every safety manager’s worst nightmare. In sectors like oil and gas, chemical processing, and mining, the presence of flammable gases, vapors, and dust creates constant risk. One small spark from non-compliant equipment can trigger catastrophic explosions, leading to devastating injuries, fatalities, and millions in damages.
The ATEX Directive1 is the European Union’s comprehensive regulatory framework that mandates strict safety standards for equipment and protective systems used in potentially explosive atmospheres. This directive ensures that all electrical and mechanical equipment meets rigorous safety requirements before being deployed in hazardous environments, significantly reducing explosion risks through proper certification and installation protocols.
I’ve spent over a decade helping companies navigate ATEX compliance challenges, and I’ve witnessed firsthand how proper understanding and implementation of these regulations can be the difference between safe operations and disaster. Let me share what every safety professional needs to know about ATEX requirements and how to achieve compliance effectively.
Table of Contents
- What Exactly is the ATEX Directive?
- Which Industries Must Comply with ATEX Requirements?
- How Do ATEX Zone Classifications Work?
- What Equipment Needs ATEX Certification?
- How Can Companies Ensure ATEX Compliance?
- FAQs About ATEX Directive
What Exactly is the ATEX Directive?
Understanding ATEX starts with recognizing its dual nature and comprehensive scope.
ATEX consists of two complementary European directives: ATEX 2014/34/EU (Equipment Directive) governing equipment design and manufacturing, and ATEX 1999/92/EC (Workplace Directive) covering workplace safety requirements. Together, these directives create a complete regulatory framework ensuring both equipment safety and proper workplace implementation.
The Historical Context
The ATEX directive emerged from tragic industrial accidents across Europe in the 1980s and 1990s. The European Union recognized that inconsistent national standards were creating safety gaps and trade barriers. By establishing unified requirements, ATEX eliminated these inconsistencies while dramatically improving safety standards.
Key Components of ATEX
The directive addresses three critical areas:
Equipment Requirements: All equipment intended for use in explosive atmospheres must undergo rigorous testing and certification by notified bodies2. This includes electrical equipment, mechanical equipment, and protective systems.
Workplace Assessment: Employers must conduct thorough risk assessments, classify hazardous areas into zones, and implement appropriate safety measures including proper equipment selection, installation, and maintenance procedures.
Conformity Procedures: Manufacturers must follow specific conformity assessment procedures, maintain technical documentation, and affix CE marking3 with ATEX symbols before placing equipment on the European market.
Which Industries Must Comply with ATEX Requirements?
ATEX compliance extends across numerous industrial sectors where explosive atmospheres may occur.
Any industry where flammable substances are present, processed, or stored must comply with ATEX requirements, including oil and gas, chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, food processing, mining, and waste treatment facilities.
Primary Industries Affected
Oil and Gas Sector: Refineries, offshore platforms, and petrochemical plants face constant exposure to hydrocarbon vapors. Every piece of electrical equipment, from cable glands to junction boxes, must meet ATEX standards.
Chemical Processing: Manufacturing facilities handling solvents, reactive chemicals, and volatile compounds require comprehensive ATEX compliance across all electrical installations.
Food and Beverage: Grain handling, sugar processing, and alcohol production create combustible dust and vapor hazards requiring specialized ATEX-certified equipment.
Real-World Implementation
Last year, I worked with Hassan, a facility manager at a major chemical plant in Rotterdam. His company was expanding their solvent processing line, and he was overwhelmed by ATEX requirements. “Chuck,” he said, “we need explosion-proof cable glands for our new installation, but I’m confused about zone classifications and certification requirements.”
We conducted a comprehensive site assessment, identifying Zone 1 and Zone 2 areas based on gas concentration probabilities. For the critical processing areas, we specified our stainless steel explosion-proof cable glands with ATEX certification, while Zone 2 areas could use our EMC cable glands with appropriate ATEX marking. The project was completed on schedule with full regulatory compliance.
How Do ATEX Zone Classifications Work?
Zone classification4 forms the foundation of ATEX compliance, determining equipment requirements based on explosion probability.
ATEX zones are classified from 0 to 2 for gases/vapors and 20 to 22 for dust, with lower numbers indicating higher explosion probability and requiring more stringent equipment protection levels.
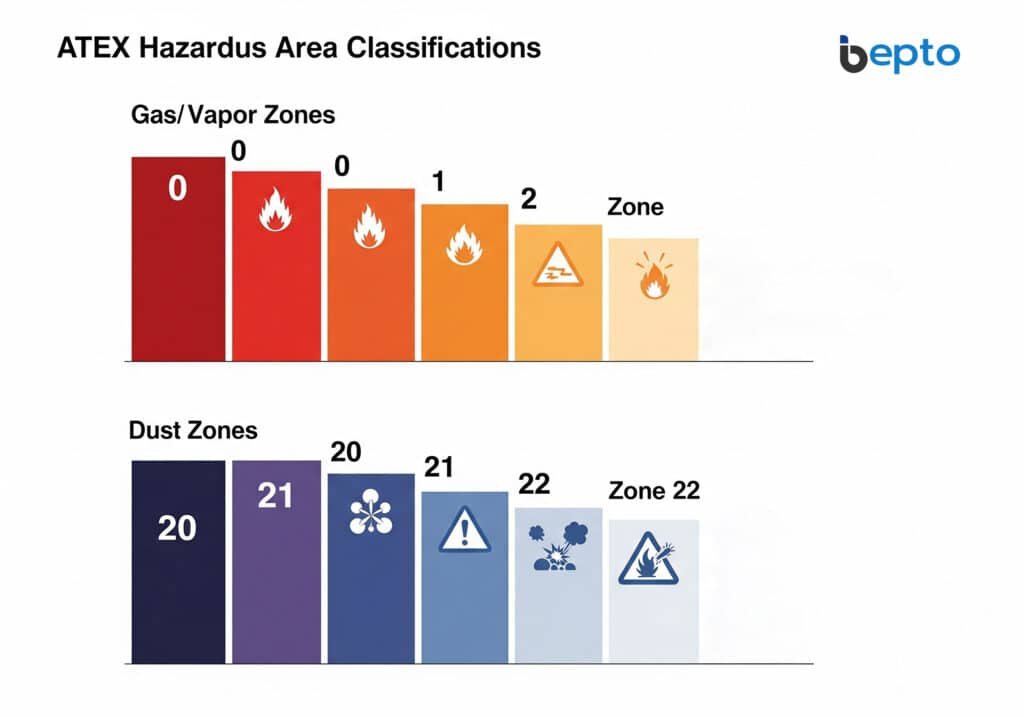
Gas and Vapor Zones
| Zone | Description | Equipment Category |
|---|---|---|
| Zone 0 | Explosive atmosphere present continuously or for long periods | Category 1G (Very High Protection) |
| Zone 1 | Explosive atmosphere likely to occur occasionally during normal operation | Category 2G (High Protection) |
| Zone 2 | Explosive atmosphere unlikely to occur, and if it does, only for short periods | Category 3G (Normal Protection) |
Dust Zones
| Zone | Description | Equipment Category |
|---|---|---|
| Zone 20 | Explosive dust atmosphere present continuously or frequently | Category 1D (Very High Protection) |
| Zone 21 | Explosive dust atmosphere likely to occur occasionally | Category 2D (High Protection) |
| Zone 22 | Explosive dust atmosphere unlikely to occur | Category 3D (Normal Protection) |
Practical Zone Assessment
Proper zone classification requires detailed analysis of process conditions, ventilation systems, and potential failure scenarios. Factors include substance properties, release probability, ventilation effectiveness, and ignition source proximity.
What Equipment Needs ATEX Certification?
ATEX certification requirements apply to a broad range of equipment used in explosive atmospheres.
All electrical equipment, mechanical equipment with potential ignition sources, and protective systems intended for use in explosive atmospheres must obtain ATEX certification before being placed on the European market.
Electrical Equipment Categories
Cable Management Systems: Cable glands, cable entries, junction boxes, and enclosures require ATEX certification when used in hazardous areas. Our explosion-proof cable glands feature robust construction with certified sealing systems preventing gas ingress.
Control and Instrumentation: Sensors, transmitters, control panels, and communication equipment must meet specific protection concepts like intrinsic safety (Ex i)5, flameproof enclosure (Ex d), or increased safety (Ex e).
Lighting and Power: Light fixtures, motors, heaters, and power distribution equipment require appropriate ATEX certification matching their intended zone application.
Protection Concepts
Different protection concepts address various ignition risks:
- Flameproof (Ex d): Enclosures withstand internal explosions without igniting external atmosphere
- Intrinsic Safety (Ex i): Circuits maintain energy levels below ignition thresholds
- Increased Safety (Ex e): Enhanced construction prevents ignition source formation
- Pressurization (Ex p): Positive pressure prevents explosive atmosphere entry
Certification Process
ATEX certification involves rigorous testing by notified bodies, including type examination, quality assurance procedures, and ongoing surveillance. Manufacturers must maintain comprehensive technical files documenting design, testing, and production quality systems.
How Can Companies Ensure ATEX Compliance?
Achieving ATEX compliance requires systematic approach combining proper assessment, equipment selection, and ongoing maintenance.
Companies ensure ATEX compliance through comprehensive hazard assessment, proper zone classification, certified equipment selection, qualified installation, regular maintenance, and ongoing staff training programs.
Step-by-Step Compliance Process
1. Hazard Assessment and Zone Classification
Conduct thorough risk assessment identifying all potential explosive atmospheres. Document substance properties, release scenarios, and environmental conditions. Classify areas into appropriate ATEX zones based on explosion probability.
2. Equipment Selection and Procurement
Select equipment with appropriate ATEX certification matching zone requirements. Verify certificates, technical documentation, and marking compliance. Ensure equipment suitability for specific environmental conditions.
3. Installation and Commissioning
Use qualified personnel for installation following manufacturer specifications and ATEX standards. Implement proper earthing, bonding, and cable management practices. Conduct thorough commissioning tests before operation.
Customer Success Story
David, a procurement manager at a North Sea oil platform, contacted me last month facing urgent ATEX compliance challenges. “Chuck, we need marine-grade explosion-proof cable glands for our drilling equipment upgrade, and time is critical,” he explained.
Understanding the harsh offshore environment, I recommended our stainless steel marine cable glands with ATEX Zone 1 certification and IP68 sealing. These glands feature corrosion-resistant construction specifically designed for offshore applications. We expedited production and delivery, ensuring his project stayed on schedule while meeting all ATEX requirements.
Ongoing Compliance Management
Documentation Management: Maintain comprehensive records of equipment certificates, installation procedures, maintenance activities, and staff training. Regular audits ensure continued compliance.
Maintenance Programs: Implement preventive maintenance programs addressing ATEX equipment specific requirements. Regular inspections identify potential issues before they compromise safety.
Training and Competency: Ensure all personnel understand ATEX requirements, zone classifications, and safe work practices. Regular training updates address regulatory changes and new technologies.
Conclusion
The ATEX directive represents one of the most comprehensive and effective explosive atmosphere safety frameworks globally. By mandating rigorous equipment certification, proper workplace assessment, and systematic compliance procedures, ATEX has dramatically reduced industrial explosion risks across Europe and beyond.
Success with ATEX compliance requires understanding both technical requirements and practical implementation challenges. From proper zone classification to certified equipment selection and ongoing maintenance, every aspect demands attention to detail and commitment to safety excellence.
As someone who has helped hundreds of companies navigate ATEX requirements, I can confidently say that proper compliance is not just about meeting regulations—it’s about protecting lives, preserving assets, and ensuring sustainable operations. The investment in ATEX-compliant equipment and procedures pays dividends through reduced risk, improved reliability, and peace of mind.
FAQs About ATEX Directive
Q: What is the difference between ATEX and IECEx certification?
ATEX is the European regulatory framework, while IECEx is the international certification scheme. ATEX certification is mandatory for European markets, while IECEx provides global recognition. Many manufacturers, including Bepto, obtain both certifications to serve international markets effectively.
Q: How often must ATEX equipment be inspected and maintained?
ATEX equipment requires regular inspection and maintenance according to manufacturer specifications and local regulations. Typically, visual inspections occur monthly, detailed inspections annually, and overhaul inspections every 3-6 years depending on equipment category and environmental conditions.
Q: Can non-ATEX certified equipment ever be used in explosive atmospheres?
No, using non-certified equipment in classified explosive atmospheres violates ATEX requirements and creates serious safety risks. All equipment must have appropriate ATEX certification matching the zone classification where it will be installed.
Q: What happens if ATEX equipment fails or is damaged?
Damaged ATEX equipment must be immediately removed from service and replaced with certified alternatives. Repairs must be performed by qualified personnel using approved procedures and materials. Equipment must be re-certified if modifications affect its explosion protection integrity.
Q: How do I verify if my supplier provides genuine ATEX certification?
Verify ATEX certification by checking the notified body number, certificate validity, and technical documentation completeness. Reputable suppliers like Bepto provide comprehensive certification packages including test reports, installation instructions, and ongoing technical support.
Q: What are the penalties for ATEX non-compliance?
ATEX non-compliance can result in significant penalties including fines, facility shutdowns, criminal liability, and insurance claim denials. More importantly, non-compliance creates serious safety risks that can lead to explosions, injuries, and fatalities.
-
Delve into the official European Commission guidelines on the ATEX Directive. ↩
-
Access the official EU NANDO database to find designated Notified Bodies for product certification. ↩
-
Learn about the requirements and significance of CE marking from the official European Union source. ↩
-
Explore a detailed guide on hazardous area zone classification from the UK’s Health and Safety Executive (HSE). ↩
-
Understand the technical principles of the ‘Intrinsic Safety (Ex i)’ protection concept in detail. ↩


